External Storage for Sample Data
Note that this requires OpenMetadata 1.2.1 or higher.
While running the auto-classification workflow if you have enabled the Generate Sample Data flag in your profiler configuration, sample data will be ingested for all the tables included in the auto-classification workflow. This data is a randomly sampled from the table and by default would contain 50 rows of data, which is now configurable.
With OpenMetadata release 1.2.1, a new capability allows users to take advantage of this sample data by uploading it to an S3 bucket in Parquet format. This means that the random sample, once generated, can be stored in a standardized, columnar storage format, facilitating efficient and scalable data analysis.
To leverage this functionality, follow the documentation provided for uploading sample data to an S3 bucket in Parquet format as part of your profiling workflow.
Configure the Sample Data Storage Credentials
To upload the sample data on you need to first configure your storage account credentials, and there are multiple ways how you can do this.
Storage Credentials at the Database Service
You can configure the Sample Data Storage Credentials at Database Service level while creating a new service or editing connection details of an existing Database Service.
You will provide the storage credential details in advance config section of connection details form.
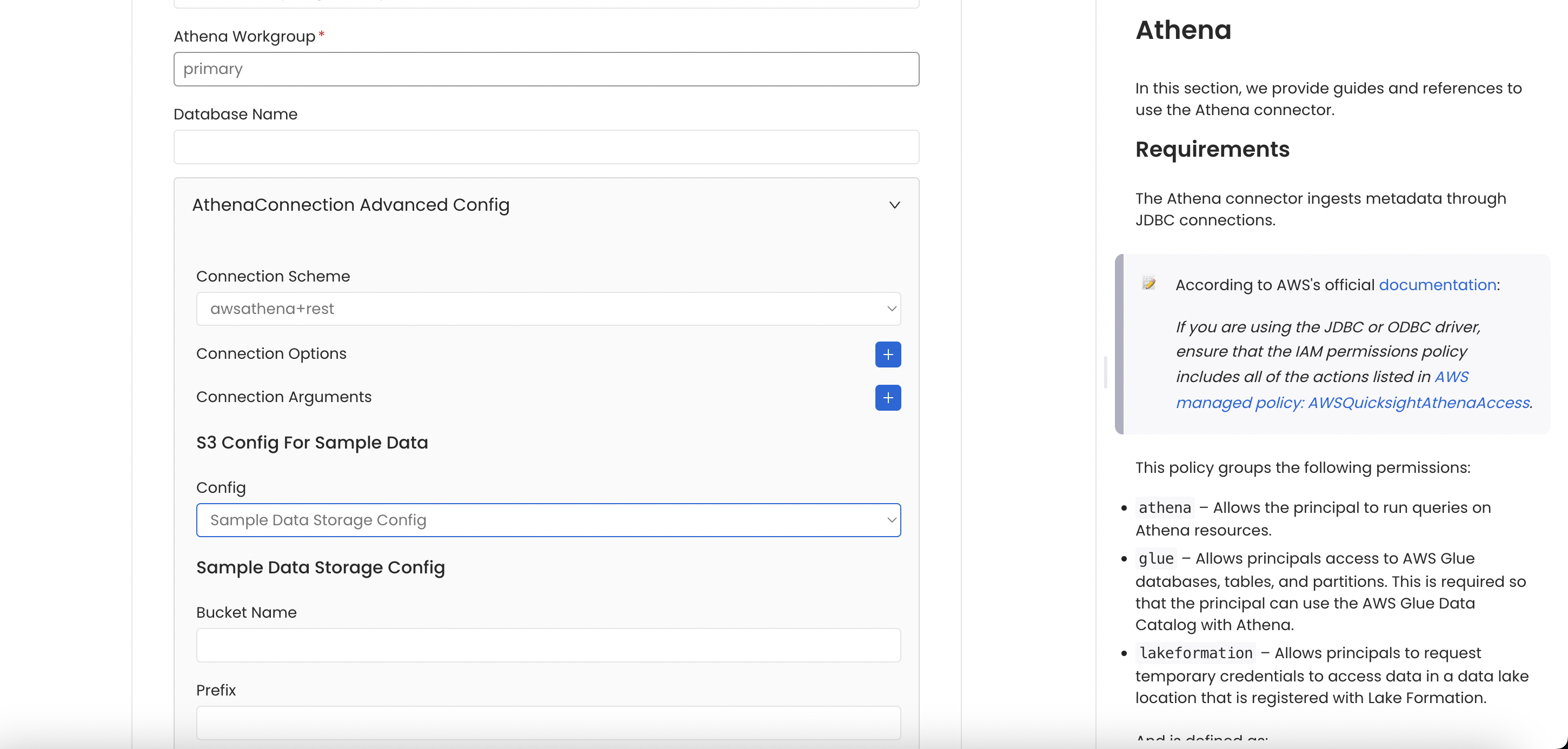
Database Service Storage Config
Storage Credentials at the Database
You can configure the Sample Data Storage Credentials at the Database level via the Profiler Settings option from the menu.
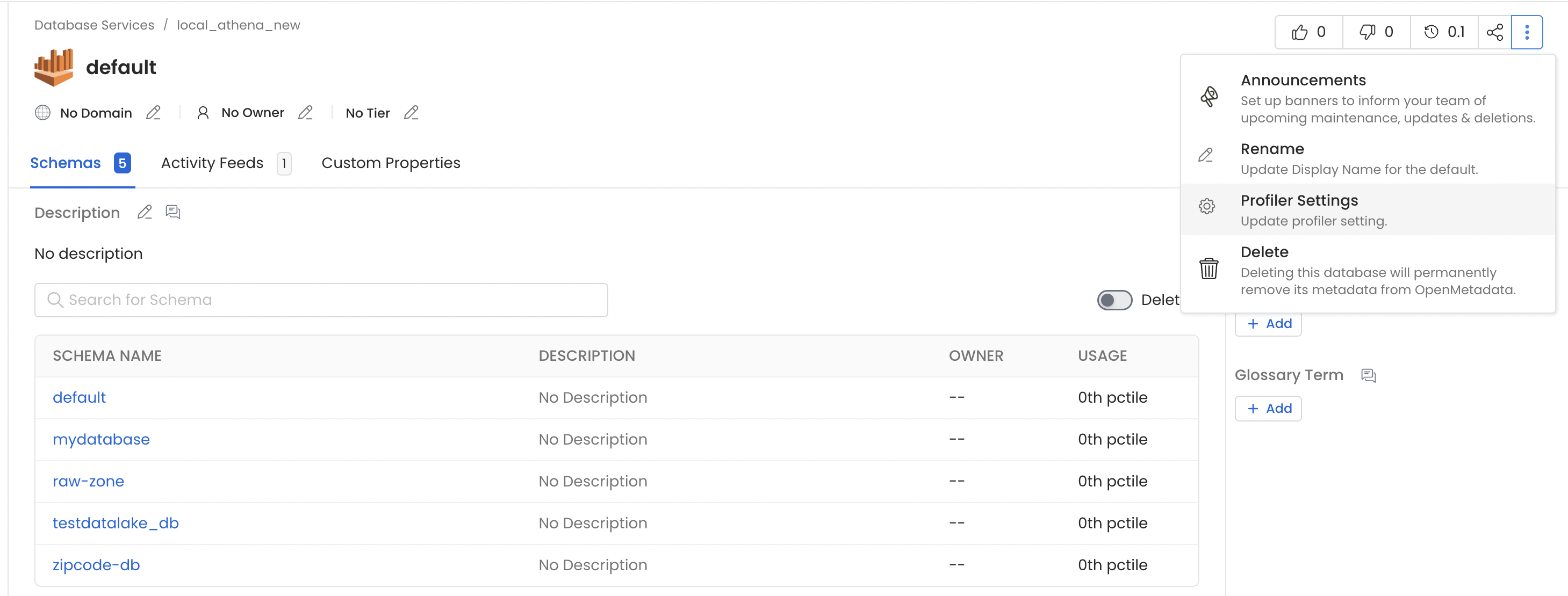
Database Storage Config - 1
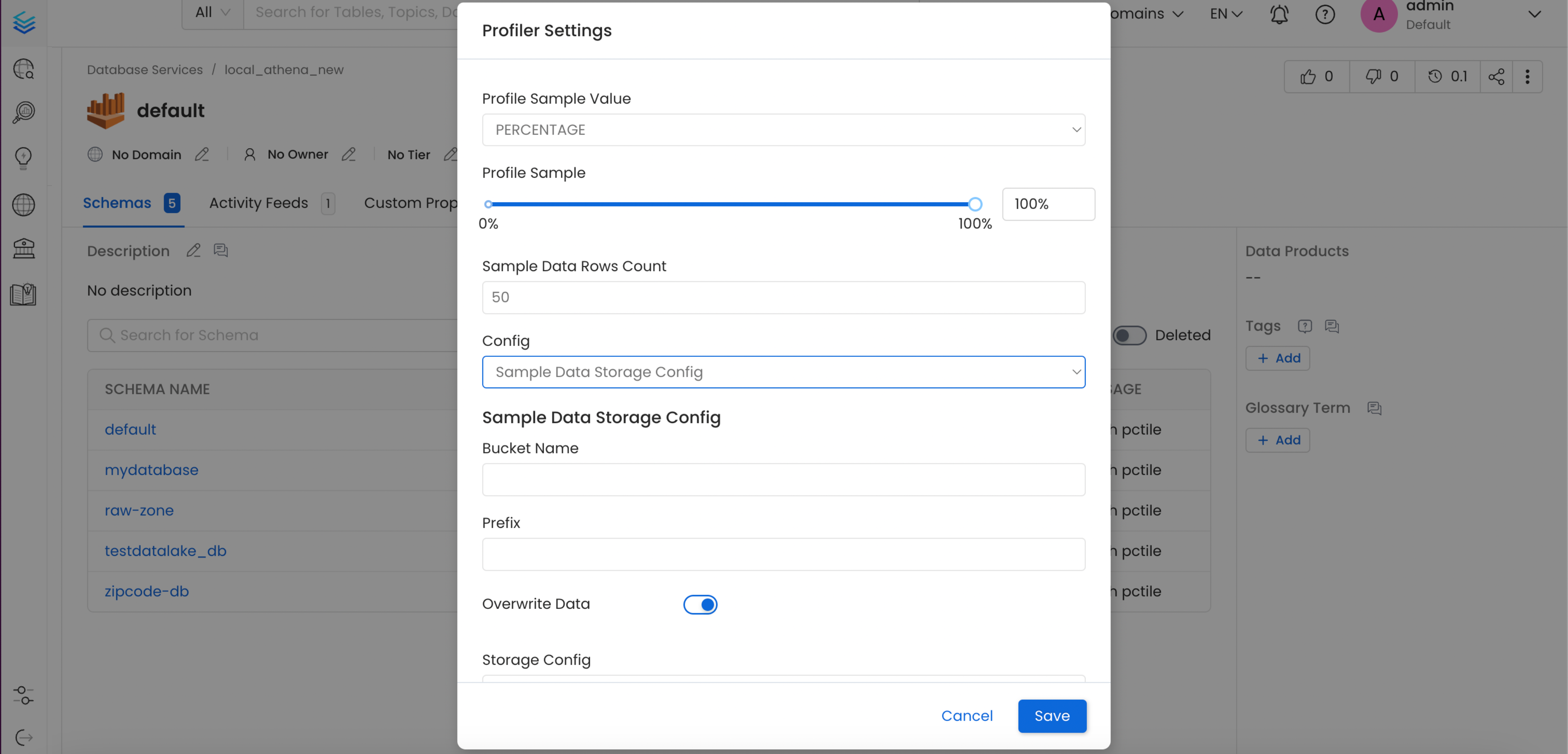
Database Storage Config - 2
Storage Credentials at the Database Schema
You can configure the Sample Data Storage Credentials at the Database Schema level via the Profiler Settings option from the menu.
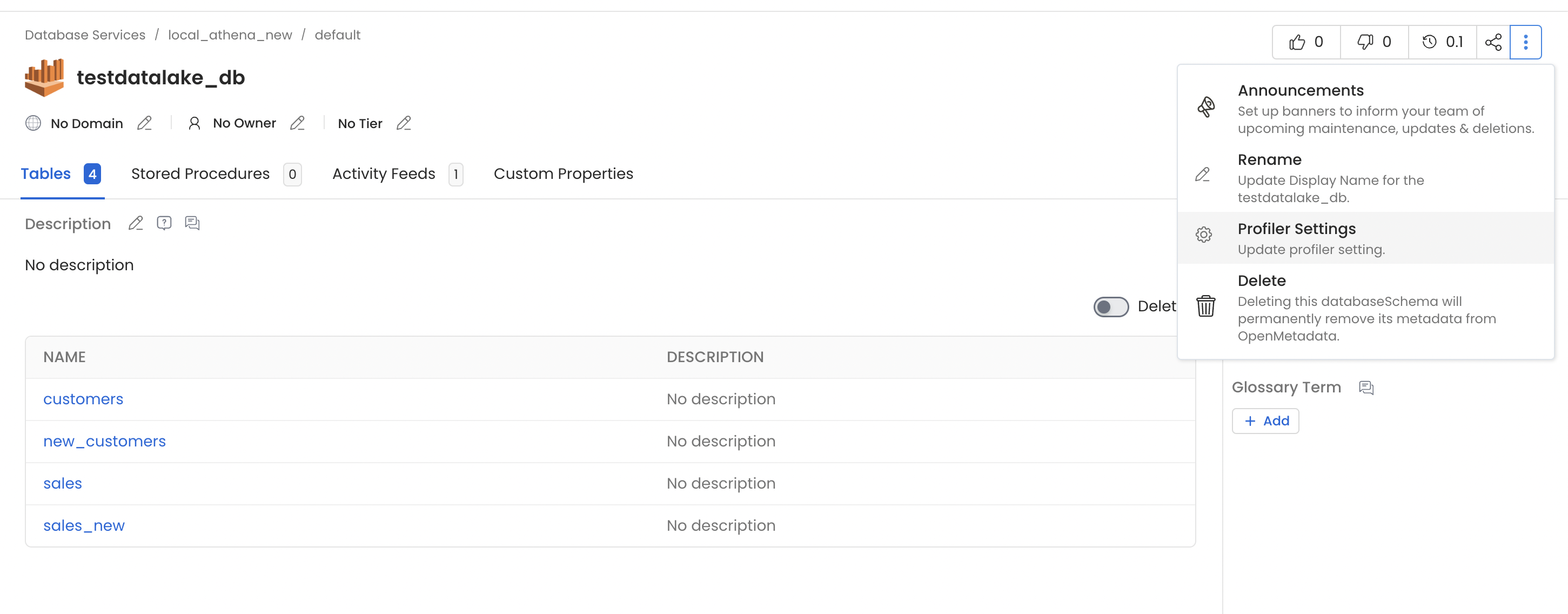
Database Schema Storage Config - 1
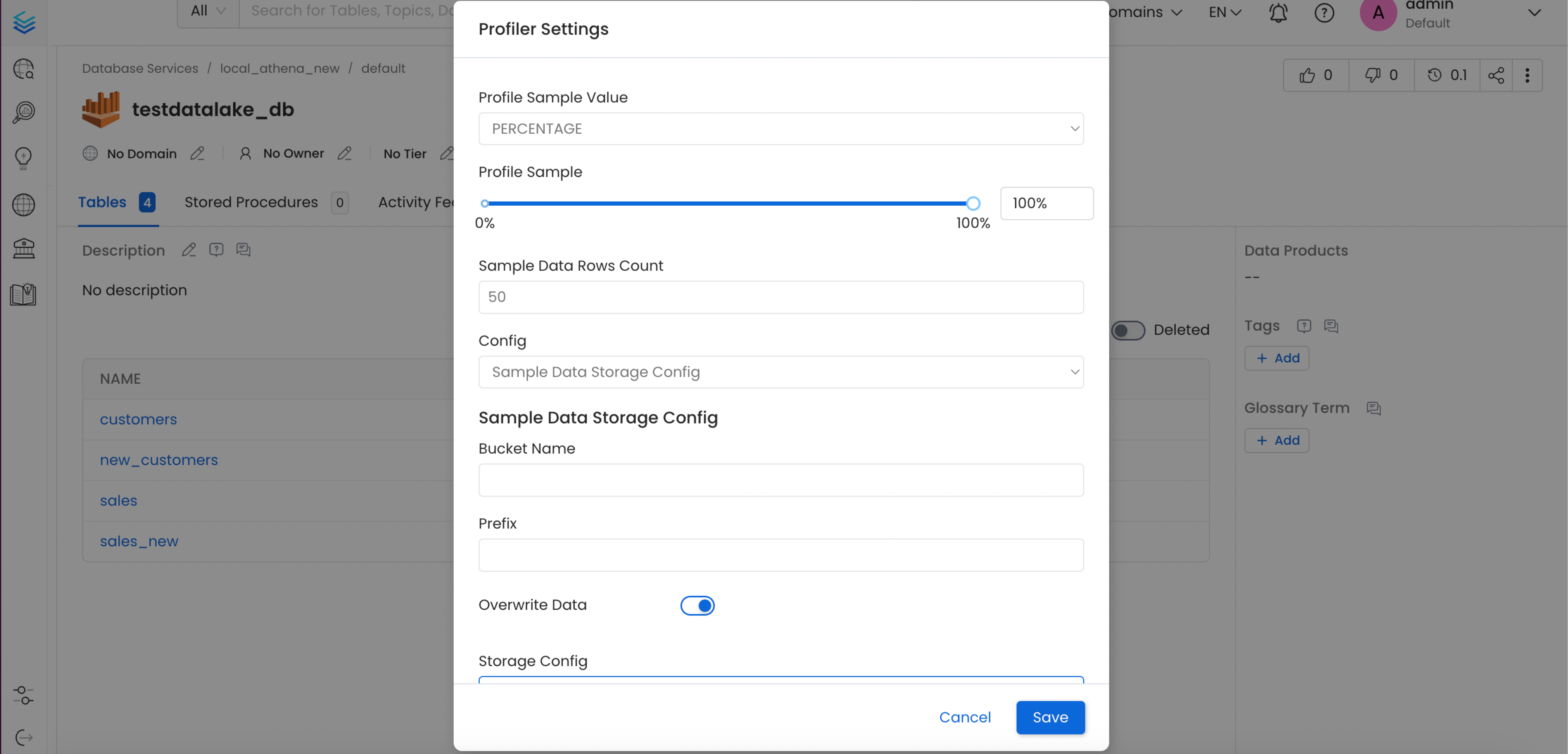
Database Schema Storage Config - 2
Configuration Details
- Profile Sample Value: Percentage of data or number of rows to use when sampling tables. By default, the profiler will run against the entire table.
- Profile Sample Type: The sample type can be set to either:
- Percentage: this will use a percentage to sample the table (e.g. if table has 100 rows, and we set sample percentage tp 50%, the profiler will use 50 random rows to compute the metrics).
- Row Count: this will use a number of rows to sample the table (e.g. if table has 100 rows, and we set row count to 10, the profiler will use 10 random rows to compute the metrics).
- Sample Data Rows Count: Number of rows of sample data to be ingested, if generate sample data option is enabled.
The OpenMetadata UI will always show 50 or fewer rows of sample data. Sample Data Rows Count higher than 50 is only used for maintaining the row count of sample data that will be stored in parquet file in an object storage.
- Sampling Method Type: The sampling method type can be set to BERNOULLI or SYSTEM. You can find the difference of two values in the document of the Snowflake. When you choice BERNOULLI, it will scan full rows in the table even though small value is set at the Profile Sample. However, it has less restlictions than SYSTEM. If no option is choiced, the default is BERNOULLI.
This parameter is effective for Snowflake only.
- Bucket Name: A bucket name is a unique identifier used to organize and store data objects. It's similar to a folder name, but it's used for object storage rather than file storage.
- Prefix: The prefix of a data source refers to the first part of the data path that identifies the source or origin of the data. The generated sample data parquet file will be uploaded to this prefix path in your bucket.
- Overwrite Sample Data: If this flag is enabled, only one parquet file will be generated per table to store the sample data. Otherwise, a parquet file will be generated for each day when the profiler workflow runs.
Connection Details for AWS S3
- AWS Access Key ID & AWS Secret Access Key: When you interact with AWS, you specify your AWS security credentials to verify who you are and whether you have permission to access the resources that you are requesting. AWS uses the security credentials to authenticate and authorize your requests (docs).
Access keys consist of two parts: An access key ID (for example, AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE), and a secret access key (for example, wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY).
You must use both the access key ID and secret access key together to authenticate your requests.
You can find further information on how to manage your access keys here.
- AWS Region: Each AWS Region is a separate geographic area in which AWS clusters data centers (docs).
As AWS can have instances in multiple regions, we need to know the region the service you want reach belongs to.
Note that the AWS Region is the only required parameter when configuring a connection. When connecting to the services programmatically, there are different ways in which we can extract and use the rest of AWS configurations.
You can find further information about configuring your credentials here.
- AWS Session Token (optional): If you are using temporary credentials to access your services, you will need to inform the AWS Access Key ID and AWS Secrets Access Key. Also, these will include an AWS Session Token.
You can find more information on Using temporary credentials with AWS resources.
- Endpoint URL (optional): To connect programmatically to an AWS service, you use an endpoint. An endpoint is the URL of the entry point for an AWS web service. The AWS SDKs and the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) automatically use the default endpoint for each service in an AWS Region. But you can specify an alternate endpoint for your API requests.
Find more information on AWS service endpoints.
- Profile Name: A named profile is a collection of settings and credentials that you can apply to a AWS CLI command. When you specify a profile to run a command, the settings and credentials are used to run that command. Multiple named profiles can be stored in the config and credentials files.
You can inform this field if you'd like to use a profile other than default.
Find here more information about Named profiles for the AWS CLI.
- Assume Role Arn: Typically, you use
AssumeRolewithin your account or for cross-account access. In this field you'll set theARN(Amazon Resource Name) of the policy of the other account.
A user who wants to access a role in a different account must also have permissions that are delegated from the account administrator. The administrator must attach a policy that allows the user to call AssumeRole for the ARN of the role in the other account.
This is a required field if you'd like to AssumeRole.
Find more information on AssumeRole.
- Assume Role Session Name: An identifier for the assumed role session. Use the role session name to uniquely identify a session when the same role is assumed by different principals or for different reasons.
By default, we'll use the name OpenMetadataSession.
Find more information about the Role Session Name.
- Assume Role Source Identity: The source identity specified by the principal that is calling the
AssumeRoleoperation. You can use source identity information in AWS CloudTrail logs to determine who took actions with a role.
Find more information about Source Identity.
OpenMetadata Storage Config
This option is useful when you want to skip uploading sample data of a schema or database from being uploaded to object storage. For example, consider the scenario where you have a database with three schemas A, B & C. You have configured the S3 Storage credentials for your database and, if you do not have any storage configuration at database schema level, then by default the sample data of the tables in the schemas will be uploaded to the storage config.
Suppose that you do not wish to upload sample data of tables from schema A, then you can choose the OpenMetadata Storage Config option to achieve the same.
Order of Precedence
As described above, you can configure the storage configuration to upload the sample data at Database Service, Database or Database Schema level. The order of precedence for selecting the storage configuration would be
Which means that if you have configured the storage credentials at database schema level, the sample data of all the tables would be uploaded with that storage config. If that is not configured, then the preference would be given to the database storage options and at last to the database service storage options.