Upgrade on Kubernetes
This guide will help you upgrade your OpenMetadata Kubernetes Application with automated helm hooks.
Requirements
This guide assumes that you have an OpenMetadata deployment that you installed and configured following the Kubernetes Deployment guide.
We also assume that your helm chart release names are openmetadata and openmetadata-dependencies and namespace used is default.
Prerequisites
Every time that you plan on upgrading OpenMetadata to a newer version, make sure to go over all these steps:
Backup your Metadata
Before upgrading your OpenMetadata version we strongly recommend backing up the metadata.
The source of truth is stored in the underlying database (MySQL and Postgres supported). During each version upgrade there is a database migration process that needs to run. It will directly attack your database and update the shape of the data to the newest OpenMetadata release.
It is important that we backup the data because if we face any unexpected issues during the upgrade process, you will be able to get back to the previous version without any loss.
You can learn more about how the migration process works here.
During the upgrade, please note that the backup is only for safety and should not be used to restore data to a higher version.
Since version 1.4.0, OpenMetadata encourages using the builtin-tools for creating logical backups of the metadata:
For PROD deployment we recommend users to rely on cloud services for their databases, be it AWS RDS, Azure SQL or GCP Cloud SQL.
If you're a user of these services, you can leverage their backup capabilities directly:
You can refer to the following guide to get more details about the backup and restore:
Understanding the Running State in OpenMetadata
In OpenMetadata, the "Running" state indicates that the OpenMetadata server has received a response from Airflow confirming that a workflow is in progress. However, if Airflow unexpectedly stops or crashes before it can send a failure status update through the Failure Callback, OpenMetadata remains unaware of the workflow’s actual state. As a result, the workflow may appear to be stuck in "Running" even though it is no longer executing.
This situation can also occur during an OpenMetadata upgrade. If an ingestion pipeline was running at the time of the upgrade and the process caused Airflow to shut down, OpenMetadata would not receive any further updates from Airflow. Consequently, the pipeline status remains "Running" indefinitely.
Running State in OpenMetadata
Expected Steps to Resolve
To resolve this issue:
- Ensure that Airflow is restarted properly after an unexpected shutdown.
- Manually update the pipeline status if necessary.
- Check Airflow logs to verify if the DAG execution was interrupted.
Update sort_buffer_size (MySQL) or work_mem (Postgres)
Before running the migrations, it is important to update these parameters to ensure there are no runtime errors. A safe value would be setting them to 20MB.
If using MySQL
You can update it via SQL (note that it will reset after the server restarts):
To make the configuration persistent, you'd need to navigate to your MySQL Server install directory and update the my.ini or my.cnf files with sort_buffer_size = 20971520.
If using RDS, you will need to update your instance's Parameter Group to include the above change.
If using Postgres
You can update it via SQL (not that it will reset after the server restarts):
To make the configuration persistent, you'll need to update the postgresql.conf file with work_mem = 20MB.
If using RDS, you will need to update your instance's Parameter Group to include the above change.
Note that this value would depend on the size of your query_entity table. If you still see Out of Sort Memory Errors during the migration after bumping this value, you can increase them further.
After the migration is finished, you can revert this changes.
Breaking Changes
- Ingestion Framework: All workflows have integrated the
workflow.print_status()inside theworkflow.execute()call. This change was needed to better handle logger lifecycles. If you’re using the Ingestion Framework directly to manage workflows via the usual process:
You can now remove the print_status() call. Note that the only side effect would be temporarily getting duplicated summary logs.
- Changed field from status to entityStatus for glossaryTerm and dataContract, as we introduce it for different data assets.
- For Data Contracts, the value also changed from Active to Approved.
MySQL Configuration Required for Airflow 3.x Migration
If you are using MySQL as your Airflow metadata database and upgrading to Airflow 3.x (the new default in OpenMetadata 1.11), you must configure MySQL to allow temporary stored function creation during the migration process.
Root Cause
During the Airflow 3.x database migration on MySQL, Airflow needs to create a temporary stored function (uuid_generate_v7) to backfill UUIDs for the task_instance table. When MySQL runs with binary logging enabled (which is the default in most production setups), it blocks function creation unless log_bin_trust_function_creators is enabled or the user has SUPER privileges. Without this configuration, the migration fails with an error like:
This is a known limitation when running Airflow 3.x migrations on MySQL with binary logging enabled. PostgreSQL users are not affected by this issue.
For more details, see the Apache Airflow issues:
Resolution
Step 1: Enable MySQL Configuration
First, enable log_bin_trust_function_creators in your MySQL instance to allow Airflow to create the necessary stored function:
For Docker deployments, add this to your docker-compose.yml file under the MySQL service:
For standalone MySQL instances, execute this query as a user with sufficient privileges:
Step 2: Clean Airflow Database
After enabling the MySQL configuration, choose one of the following options based on your situation:
Option 1: Clean Airflow Metadata (Recommended for Fresh Start)
If you want to avoid conflicting migration changes and start with a clean Airflow metadata database, you can truncate the task_instance table. This approach removes all task execution history but preserves your DAGs and connections.
This will delete all historical task execution data. Only use this if you're okay with losing task run history.
Execute this script:
Option 2: Fix Stuck Migrations (If Migration Already Failed)
If your migration is already stuck midway (the task_instance table was partially modified), you need to reset the migration state before restarting. Save the following SQL script as fix_airflow_migration.sql:
Then execute the script and restart the container:
Replace USERNAME and PASSWORD with your actual MySQL credentials, and ensure the database name matches your configuration (default is airflow_db).
Breaking Changes
Helm Chart Refactor (v1.11.0)
OpenMetadata v1.11.0 includes a major refactor of the Helm charts as part of PR #430. This introduces several breaking changes that require manual intervention for existing deployments.
Airflow Chart Migration
The Helm chart has migrated from the community airflow-helm/airflow v8.9.0 chart to the official Apache airflow v1.18.0 chart. This results in:
- Complete Values Restructure: The Airflow configuration in
values.yamlhas been entirely reorganized to match the Apache Airflow Helm chart structure. - Service Endpoint Changes: Airflow services have been renamed (e.g.,
webservice is nowapi-server). - Chart Dependency Changes: The underlying chart dependency has changed completely.
Required Migration Steps
If you are upgrading from a previous version with openmetadata-dependencies deployed, follow these steps:
- Backup your Airflow data - Ensure you have backups of your Airflow database and any custom configurations.
- Uninstall the existing
openmetadata-dependenciesrelease: - Update Helm dependencies:
- Install the new chart version - Follow the installation steps in Step 3.
- Update OpenMetadata configuration - Update any service endpoint references in your OpenMetadata configuration (see below).
Configuration Changes
Service Endpoints
Update any Airflow service endpoint references from:
To:
In your OpenMetadata values file, update the pipelineServiceClientConfig.apiEndpoint:
Executor Configuration
The default executor is now KubernetesExecutor (recommended for production). If you need to use LocalExecutor for development:
Webserver Secret Key
A static webserverSecretKey is now required to prevent JWT authentication failures between Airflow components (scheduler, api-server, and workers).
Generate a secure key and add it to your values:
Database Connection Structure
Database connections have migrated from an embedded format to the Apache chart structure with separate fields:
MySQL Compatibility
If using MySQL as the Airflow metadata database, the chart includes a compatibility workaround for MySQL syntax issues:
This is automatically included in the default values to resolve CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS syntax compatibility.
Upgrade Process
Step 1: Get an overview of what has changed in Helm Values
You can get changes from artifact hub of openmetadata helm chart release. Click on Default Values >> Compare to Version.
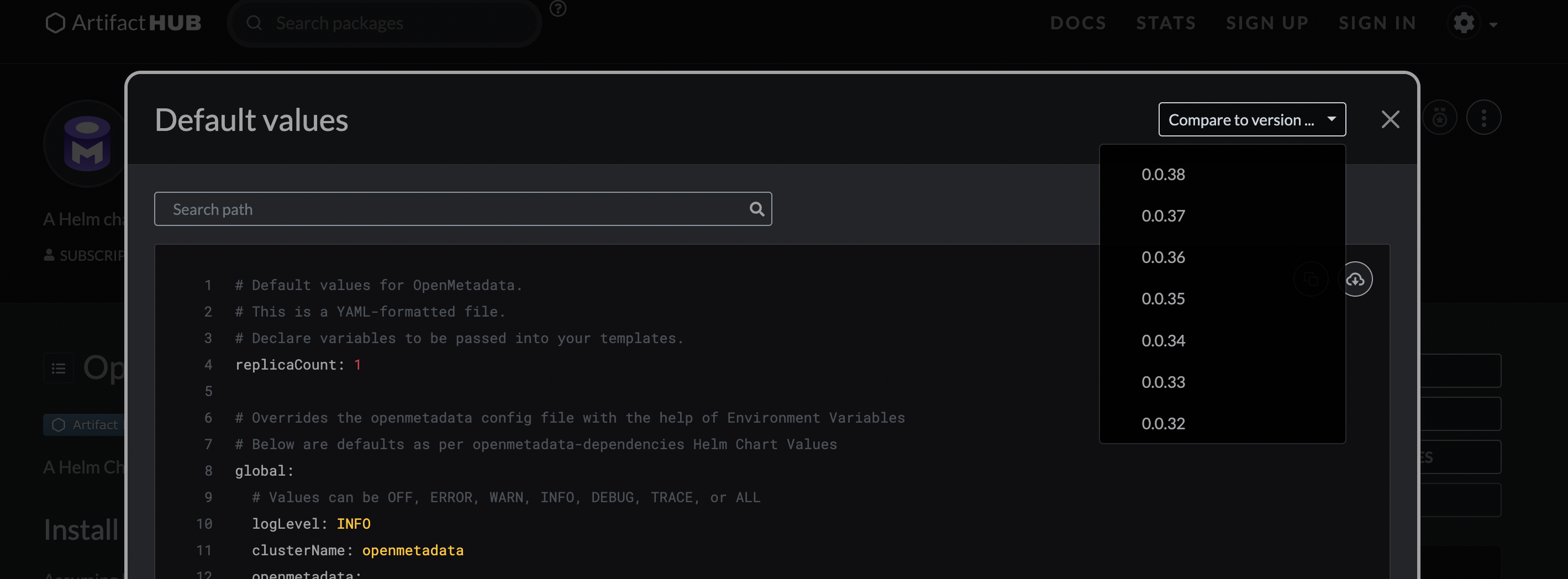
Step 2: Upgrade Helm Repository with a new release
Update Helm Chart Locally for OpenMetadata with the below command:
It will result in the below output on screen.
Verify with the below command to see the latest release available locally.
Step 3: Upgrade OpenMetadata Dependencies
You can run the below command to upgrade the dependencies with the new chart
The above command uses configurations defined here. You can modify any configuration and deploy by passing your own values.yaml.
Make sure that, when using your own values.yaml, you are not overwriting elements such as the image of the containers. This would prevent your new deployment to use the latest containers when running the upgrade.
If you are running into any issues, double-check what are the default values of the helm revision.
Step 4: Upgrade OpenMetadata
Finally, we upgrade OpenMetadata with the below command:
You might need to pass your own values.yaml with the --values flag.
Note that in every version upgrade there is a migration process that updates your database to the newest version.
For kubernetes, this process will happen automatically as an upgrade hook.
You can learn more about how the migration process works here.
Post-Upgrade Steps
Reindex
With UI
Go to Settings -> Applications -> Search Indexing
Reindex
Before initiating the process by clicking Run Now, ensure that the Recreate Indexes option is enabled to allow rebuilding the indexes as needed.
In the configuration section, you can select the entities you want to reindex.
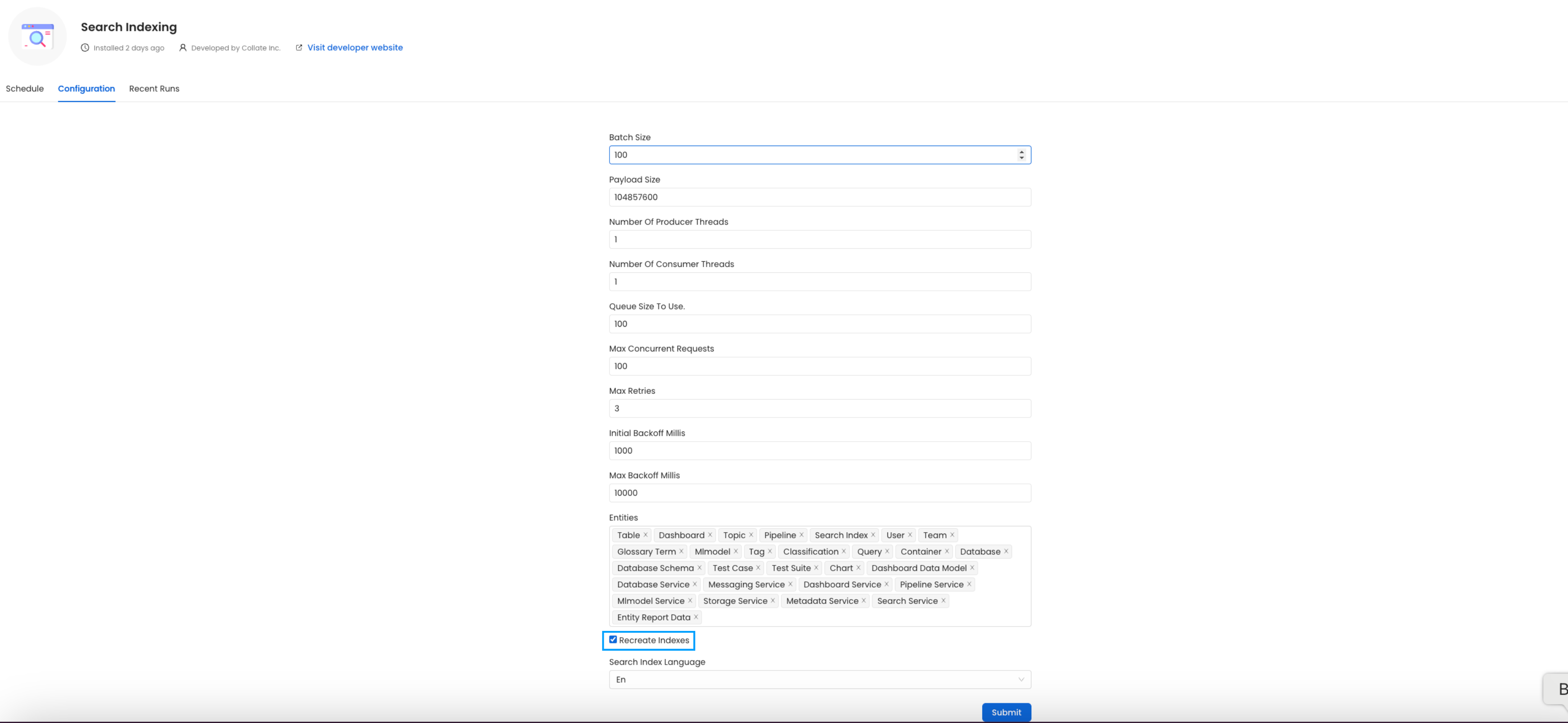
Reindex
Since this is required after the upgrade, we want to reindex All the entities.
(Optional) Update your OpenMetadata Ingestion Client
If you are running the ingestion workflows externally or using a custom Airflow installation, you need to make sure that the Python Client you use is aligned with the OpenMetadata server version.
For example, if you are upgrading the server to the version x.y.z, you will need to update your client with
With Kubernetes
Follow these steps to reindex using the CLI:
- List the CronJobs Use the following command to check the available CronJobs:
Upon running this command you should see output similar to the following.
- Create a Job from a CronJob Create a one-time job from an existing CronJob using the following command:
Replace <job_name> with the actual name of the job.
Upon running this command you should see output similar to the following.
- Check the Job Status Verify the status of the created job with:
Upon running this command you should see output similar to the following.
- view logs To view the logs use the below command.
Replace <job_name> with the actual job name.
The plugin parameter is a list of the sources that we want to ingest. An example would look like this openmetadata-ingestion[mysql,snowflake,s3]==1.2.0. You will find specific instructions for each connector here.
Moreover, if working with your own Airflow deployment - not the openmetadata-ingestion image - you will need to upgrade as well the openmetadata-managed-apis version:
Re Deploy Ingestion Pipelines
With UI
Go to Settings -> {Services} -> {Databases} -> Pipelines
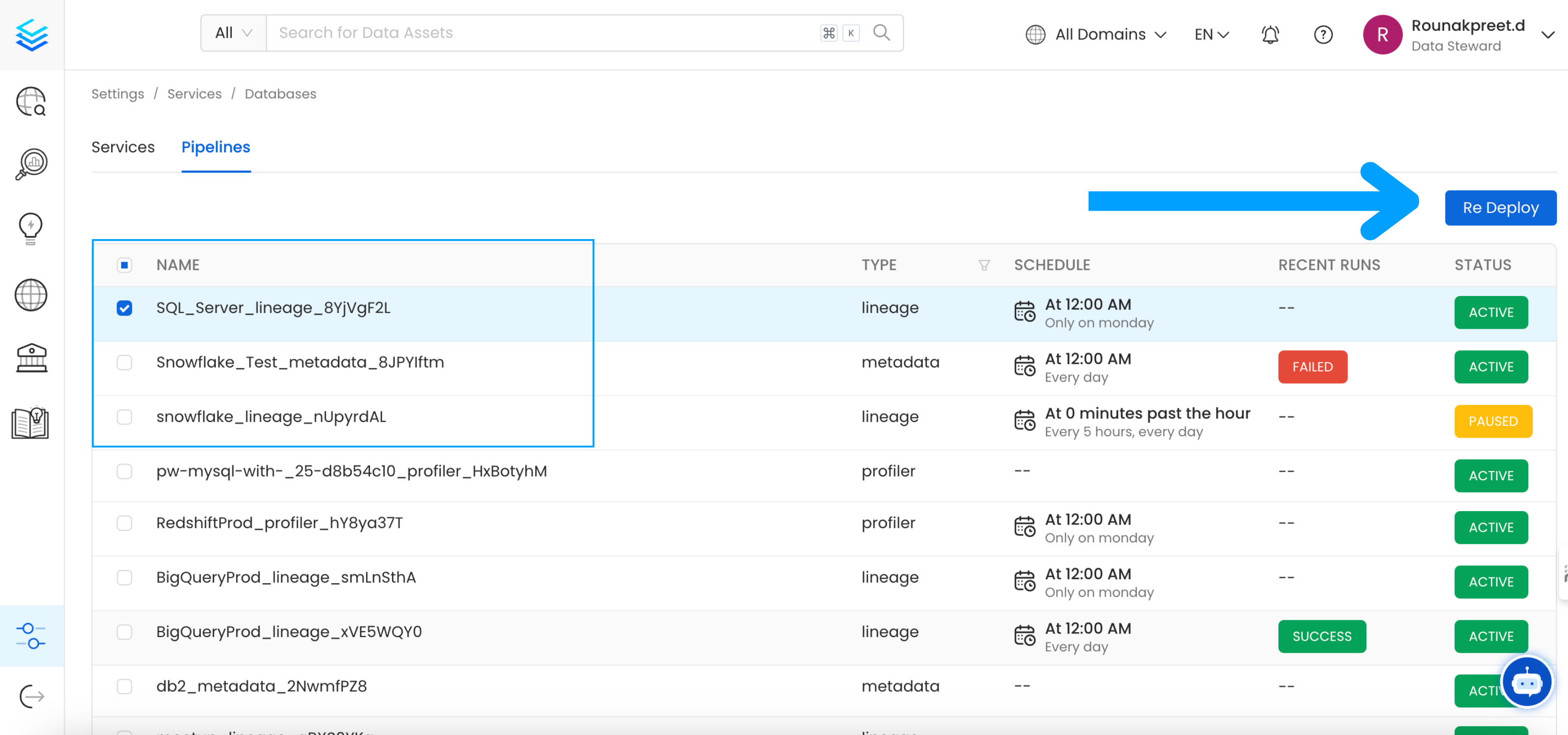
Re-deploy
Select the pipelines you want to Re Deploy click Re Deploy.
With Kubernetes
Follow these steps to deploy pipelines using the CLI:
- List the CronJobs Use the following command to check the available CronJobs:
Upon running this command you should see output similar to the following.
- Create a Job from a CronJob Create a one-time job from an existing CronJob using the following command:
Replace <job_name> with the actual name of the job.
Upon running this command you should see output similar to the following.
- Check the Job Status Verify the status of the created job with:
Upon running this command you should see output similar to the following.
- view logs To view the logs use the below command.
Replace <job_name> with the actual job name.
If you are seeing broken dags select all the pipelines from all the services and re deploy the pipelines.
Openmetadata-ops Script
Overview
The openmetadata-ops script is designed to manage and migrate databases and search indexes, reindex existing data into Elastic Search or OpenSearch, and redeploy service pipelines.
Usage
Commands
- analyze-tables
Migrates secrets from the database to the configured Secrets Manager. Note that this command does not support migrating between external Secrets Managers.
- changelog
Prints the change log of database migration.
- check-connection
Checks if a connection can be successfully obtained for the target database.
- deploy-pipelines
Deploys all the service pipelines.
- drop-create
Deletes any tables in the configured database and creates new tables based on the current version of OpenMetadata. This command also re-creates the search indexes.
- info
Shows the list of migrations applied and the pending migrations waiting to be applied on the target database.
- migrate
Migrates the OpenMetadata database schema and search index mappings.
- migrate-secrets
Migrates secrets from the database to the configured Secrets Manager. Note that this command does not support migrating between external Secrets Managers.
- reindex
Reindexes data into the search engine from the command line.
- repair
Repairs the DATABASE_CHANGE_LOG table, which is used to track all the migrations on the target database. This involves removing entries for the failed migrations and updating the checksum of migrations already applied on the target database.
- validate
Checks if all the migrations have been applied on the target database.
Examples
Display Help To display the help message:
Migrate Database Schema
To migrate the database schema and search index mappings:
Reindex Data
To reindex data into the search engine:
Troubleshooting
Helm Upgrade failed for Airflow 3 Upgrade
If you see a similar issue as above when migrating OpenMetadata Helm Chart to latest 1.11.X Release, this is because Kubernetes does not allow updating Persistent volume claim fields. You need to uninstall openmtadata-dependencies helm chart as mentioned in the above steps here (point 2). Uninstalling the openmetadata-dependencies helm chart will remove the PVCs and upon re-install of helm chart with latest 1.11.X Release, the chart will recreate the PVCs required. You will need to perform Post upgrade steps to redeploy pipelines to add the previous pipelines to Airflow as DAGs.
Helm Upgrade fails with additional property airflow not allowed
With Release 1.0.0, if you see your helm charts failing to deploy with the below issue -
This means the values passed to the helm charts has a section global.airflow. Airflow configs are replaced with pipelineServiceClient for Helm Charts.
The Helm Chart Values JSON Schema helps to catch the above breaking changes and this section will help you resolve and update your configurations for the same. You can read more about JSON Schema with Helm Charts here.
You will need to update the existing section of global.airflow values to match the new configurations.
⛔ Before 1.0.0 Helm Chart Release, the global.airflow section would be like -
✅ After 1.0.0 Helm Chart Release, the global.pipelineServiceClient section will replace the above airflow section -
Run the helm lint command on your custom values after making the changes to validate with the JSON Schema.
MySQL Pod fails on Upgrade
This issue will only occur if you are using openmetadata-dependencies helm chart version 0.0.49 and 0.0.50 and upgrading to latest helm chart release.
If your helm dependencies upgrade fails with the below command result -
This issue is related to a minor change that affected the MySQL Database Engine version upgrade from 8.0.28 to 8.0.29 for the Helm Chart Release 0.0.49 and 0.0.50. Then the registry url was updated as we found a work around to fetch previous versions of bitnami/mysql Helm Releases.
As a result of the above fixes, anyone who is on OpenMetadata Dependencies Helm Chart Version 0.0.49 and 0.0.50 is affected with the above issue when upgrading for mysql. In order to fix this issue, make sure to follow the below steps -
- Backup the Database using Metadata Backup CLI as mentioned here
- Uninstall OpenMetadata Dependencies Helm Chart (
helm uninstall openmetadata-dependencies) - Remove the unmanaged volume for MySQL Stateful Set Kubernetes Object (
kubectl delete pvc data-mysql-0) - Install the latest version of OpenMetadata Dependencies Helm Chart
- Restore the Database using Metadata Restore CLI as mentioned here
- Next, Proceed with upgrade for OpenMetadata Helm Chart as mentioned here
Azure PostgreSQL Extension Issue During 1.11.0 Migration
During the 1.11.0 database migration, OpenMetadata attempts to execute the following SQL command:
However, when using Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server, extensions like pg_trgm must be explicitly allow-listed by the administrator.
Since pg_trgm is not allow-listed by default, Azure returns the following error:
This error causes the migration to fail before completing the schema updates.
Recommended Action Ensure that the pg_trgm extension is added to the allow-list in your Azure PostgreSQL server settings prior to running the migration.