Google SSO Configuration - Confidential Client
This configuration is required for web applications and backend services that can securely store client credentials.
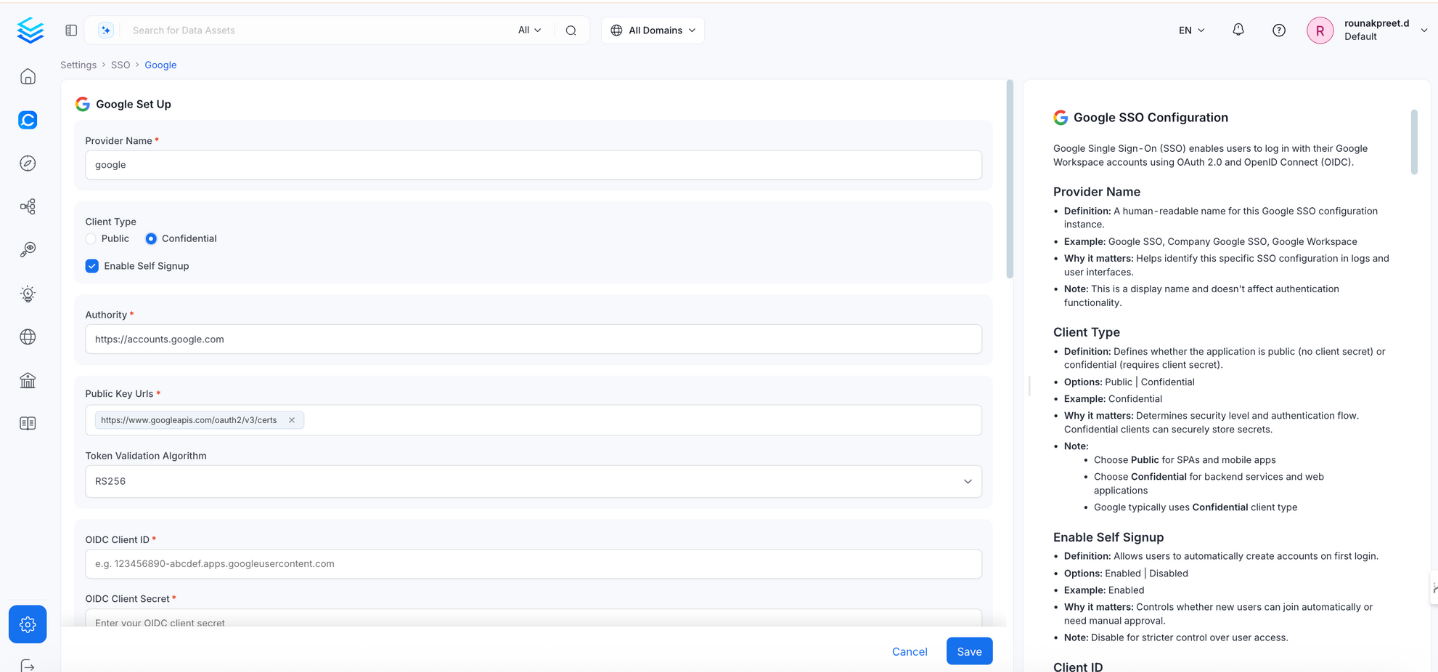
1. Enable Self Signup
- Definition: Allows users to automatically create accounts on first login.
- Options:
Enabled|Disabled - Example:
Enabled - Why it matters: Controls whether new users are auto-created.
- Note: Set to
Disabledfor stricter access control.
2. Authority
- Definition: Google’s OAuth 2.0 authorization server.
- Default & Example:
https://accounts.google.com - Why it matters: Specifies where OpenMetadata should send auth requests.
- Note: Usually does not need to be changed.
3. Public Key URLs
- Definition: URL(s) where Google publishes its JWT signing keys.
- Example:
["https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v3/certs"] - Why it matters: Required to verify JWT token signatures.
- Note: Typically auto-discovered via OIDC discovery endpoint.
4. Token Validation Algorithm
- Definition: Algorithm used to validate JWT tokens.
- Options:
RS256|RS384|RS512 - Default & Example:
RS256 - Why it matters: Must match Google’s signing algorithm.
- Note: Google typically uses
RS256.
5. OIDC Client ID
- Definition: OAuth 2.0 Client ID from Google Cloud Console.
- Example:
123456789012-abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz123456.apps.googleusercontent.com - Why it matters: Uniquely identifies the app in the OIDC flow.
6. OIDC Client Secret
- Definition: Confidential key used to authenticate the app with Google.
- Example:
GOCSPX-abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz123456 - Why it matters: Required for token exchange.
- Note:
- Found in Google Cloud Console > Credentials.
- Store securely and rotate periodically.
7. OIDC Request Scopes
- Definition: Permissions to request from Google during login.
- Default: openid email profile
- Example:
openid email profile https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email - Why it matters: Determines what user information is accessible.
8. OIDC Discovery URI
- Definition: Google OIDC metadata URL.
- Example:
https://accounts.google.com/.well-known/openid-configuration - Why it matters: Enables OpenMetadata to auto-discover endpoints.
9. OIDC Use Nonce
- Definition: Prevents replay attacks.
- Default & Example:
true - Why it matters: Enhances session-level security.
10. OIDC Preferred JWS Algorithm
- Default & Example:
RS256 - Why it matters: Must match Google's token signing algorithm.
11. OIDC Response Type
- Definition: Type of OAuth response expected.
Options: id_token | code
- Default & Example:
code - Why it matters: Defines OAuth flow; code is more secure.
12. OIDC Disable PKCE
- Definition: Disables Proof Key for Code Exchange.
- Default & Example:
false - Why it matters: PKCE adds protection to authorization code flow.
13. OIDC Max Clock Skew
- Definition: Allowed time difference between systems.
- Example:
0 - Why it matters: Prevents token validation issues due to clock drift.
14. OIDC Client Authentication Method
- Options: client_secret_basic, client_secret_post, client_secret_jwt, private_key_jwt
- Default & Example:
client_secret_basic - Why it matters: Defines how the client secret is passed to Google.
15. OIDC Token Validity
- Default: 0 (use provider default)
- Example:
3600 (1 hour) - Why it matters: Sets how long a token is valid.
16. OIDC Callback URL
- Definition: Redirect URL where Google sends authentication responses.
- Example:
https://yourapp.company.com/callback - Why it matters: Must match exactly with Google Cloud Console’s registered redirect URL.
- Note:
- Must be registered under OAuth 2.0 Client > Authorized Redirect URLs.
- Always use HTTPS in production.
17. OIDC Max Age
- Definition: Maximum age of authentication before re-auth is required.
- Example:
3600 - Why it matters: Controls session longevity.
18. OIDC Prompt
- Options: none, login, consent, select_account
- Example:
select_account - Why it matters: Adjusts user experience during login.
- Note:
- login: Always prompt credentials.
- consent: Ask user for permission.
- select_account: Display account picker.
- none: Attempt silent login (may fail if not authenticated).
19. OIDC Session Expiry
- Default: 604800 (7 days)
- Example:
604800 - Why it matters: Defines how long the user stays logged in.
20. JWT Principal Claims Mapping
- Definition: Maps JWT claims to OpenMetadata user attributes.
- Example:
- Why it matters: Maps identity information to OpenMetadata user profiles.
- Note: Use the format
openmetadata_field:jwt_claim.
21. Admin Principals
- Definition: List of email addresses with admin access.
- Example:
["admin@company.com", "superuser@company.com"] - Why it matters: Grants admin-level privileges in the system.
- Note: Email must match a JWT claim.
22. Principal Domain
- Definition: Default domain for constructing user emails.
- Example:
company.com - Why it matters: Helps form complete user identifiers from partial input.
- Note: Matches your Google Workspace domain.
23. Enforce Principal Domain
- Definition: Restrict login to users from a specific domain.
- Default: false
- Example:
true - Why it matters: Adds domain-level access control.
- Note: Use with hd parameter in custom OIDC config.
24. Enable Secure Socket Connection
- Definition: Enables SSL/TLS for secure communications.
- Default: false
- Example:
true - Why it matters: Ensures secure token exchange and communication.
- Note: Must be true in production.
Troubleshooting
If users are automatically logged out and unable to log in again due to a bad authentication configuration, you can reset the security setup using the following command:
After executing the command, restart the server. The authentication values from your YAML or Helm chart will then be reapplied on startup. The following tiles detail how to apply this configuration across Docker, Kubernetes, and Bare Metal deployments: