Reindexing Search
If you are encountering any of the following issues:
- Mismatch in counts of Data Assets.
- Data not appearing.
- Errors such as
shards_exception. - Problems with the search mechanism.
- Empty results in the Explore section.
- Missing lineage information.
Perform the reindexing process described below.
Reindex
Go to Settings -> Applications -> Search Indexing
Reindex
Before initiating the process by clicking Run Now, ensure that the Recreate Indexes option is enabled to allow rebuilding the indexes as needed.
In the configuration section, you can select the entities you want to reindex.
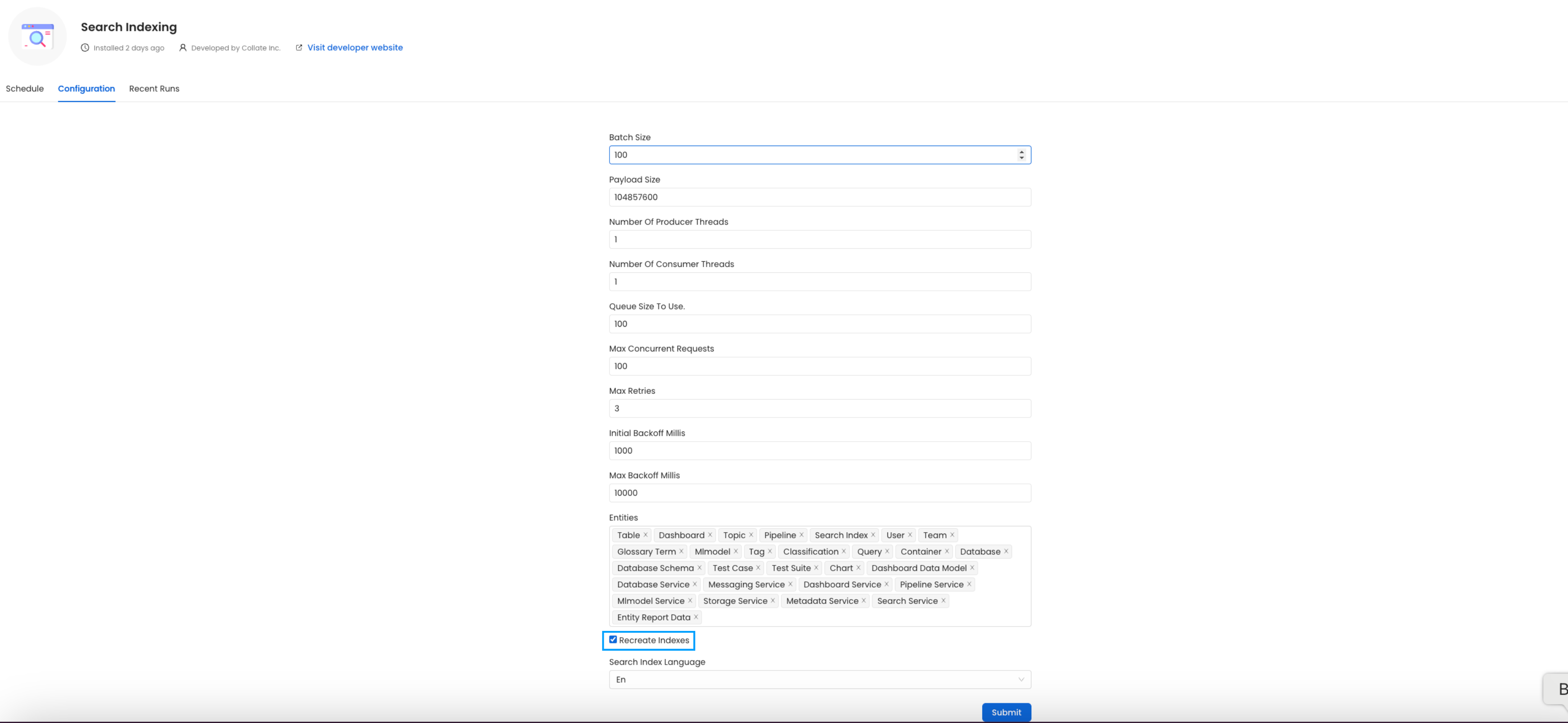
Reindex
Note: If you continue to experience issues, consider re-installing the search application.
Configuration Parameters for Reindexing
This document provides detailed descriptions and best practices for configuring the reindexing process parameters. Proper configuration ensures efficient and reliable reindexing while minimizing potential system bottlenecks.
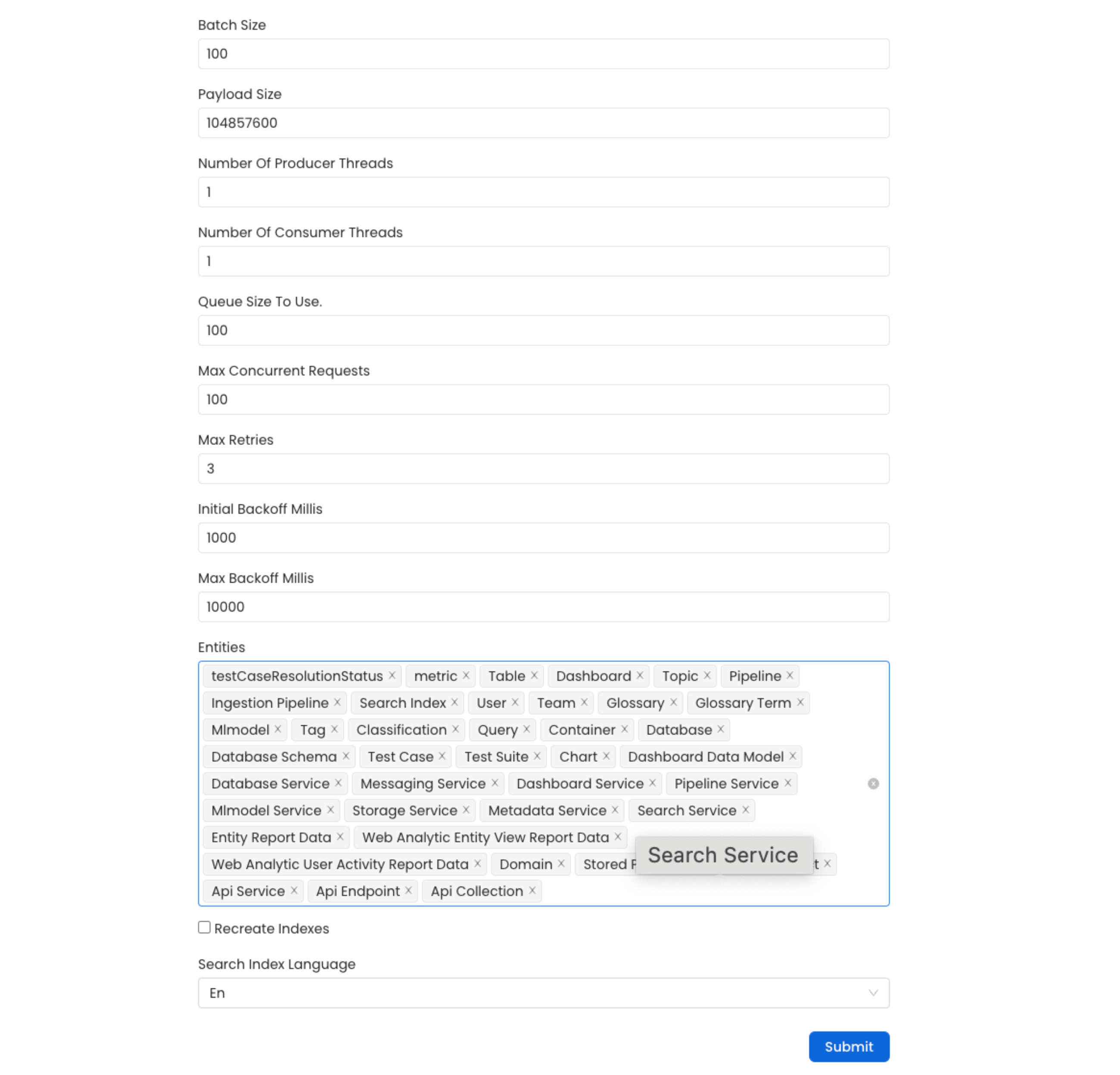
1. recreateIndex
Description:
Determines whether to recreate the index from scratch during the reindexing process. Setting this to true will drop the existing index and create a new one.
Best Practice:
Use this option with caution. Set it to true only when you need a clean slate, such as after significant changes to your data model or during data migration. For routine updates, keep it false to preserve the existing index.
2. batchSize
Description:
Defines the maximum number of events sent in a single batch during reindexing. The default value is 100.
Best Practice:
Adjust the batch size based on system capabilities and event size. A larger batch size improves throughput but may increase memory usage and processing time. Monitor performance and fine-tune accordingly.
3. payLoadSize
Description:
Specifies the maximum payload size (in bytes) for events sent in a batch. Default: 104,857,600 bytes (100 MB).
Best Practice:
Ensure the payload size is within your system’s handling capacity. If memory issues or timeouts occur, reduce this value to improve stability.
4. producerThreads
Description:
Indicates the number of threads used for producing events during reindexing. Default: 10.
Best Practice:
Balance the number of threads with system CPU and I/O capacity. Increasing this number can improve throughput but may lead to contention if set too high.
5. maxConcurrentRequests
Description:
Specifies the maximum number of concurrent requests sent to the search index at any given time. Default: 100.
Best Practice:
Tune this value based on the indexing server’s capacity. Too many concurrent requests can overwhelm the server, leading to failures or slowdowns.
6. maxRetries
Description:
Specifies the maximum number of retry attempts for failed requests. Default: 3 retries.
Best Practice:
Keep this value reasonable to avoid excessive load during failures. Analyze failure patterns to optimize this setting.
7. initialBackoff
Description:
Defines the initial backoff time (in milliseconds) before retrying a failed request. Default: 1000 ms (1 second).
Best Practice:
Start with the default value. Increase it if failures occur frequently due to server overload or network issues.
8. maxBackoff
Description:
Specifies the maximum backoff time (in milliseconds) for retries. Default: 10,000 ms (10 seconds).
Best Practice:
Set this value to align with your application’s latency tolerance. A longer backoff can reduce system load during peak times but may slow recovery from errors.
9. queueSize
Description:
Defines the internal queue size used for reindexing operations. Default: 100.
Best Practice:
Adjust the queue size based on expected load and available memory resources. A larger queue can handle spikes in processing but requires more memory.
Example Configuration for Best Practices
For high-performance systems, consider the following values as a starting point:
Monitor system performance and adjust these parameters to optimize throughput and resource usage.