Sagemaker
PRODIn this section, we provide guides and references to use the Sagemaker connector.
Configure and schedule Sagemaker metadata and profiler workflows from the OpenMetadata UI:
Ingestion Deployment
To run the Ingestion via the UI you'll need to use the OpenMetadata Ingestion Container, which comes shipped with custom Airflow plugins to handle the workflow deployment. If you want to install it manually in an already existing Airflow host, you can follow this guide.
If you don't want to use the OpenMetadata Ingestion container to configure the workflows via the UI, then you can check the following docs to run the Ingestion Framework in any orchestrator externally.
Run Connectors from the OpenMetadata UI
Learn how to manage your deployment to run connectors from the UIRun the Connector Externally
Get the YAML to run the ingestion externallyExternal Schedulers
Get more information about running the Ingestion Framework ExternallyRequirements
OpenMetadata retrieves information about models and tags associated with the models in the AWS account. The user must have the following policy set to ingest the metadata from Sagemaker.
For more information on Sagemaker permissions visit the AWS Sagemaker official documentation.
Metadata Ingestion
1. Visit the Services Page
Click Settings in the side navigation bar and then Services.
The first step is to ingest the metadata from your sources. To do that, you first need to create a Service connection first.
This Service will be the bridge between OpenMetadata and your source system.
Once a Service is created, it can be used to configure your ingestion workflows.
Select your Service Type and Add a New Service
Add a new Service from the Services page
Select your Service from the list
4. Name and Describe your Service
Provide a name and description for your Service.
Service Name
OpenMetadata uniquely identifies Services by their Service Name. Provide a name that distinguishes your deployment from other Services, including the other SageMaker Services that you might be ingesting metadata from.
Note that when the name is set, it cannot be changed.
Provide a Name and description for your Service
5. Configure the Service Connection
In this step, we will configure the connection settings required for SageMaker.
Please follow the instructions below to properly configure the Service to read from your sources. You will also find helper documentation on the right-hand side panel in the UI.
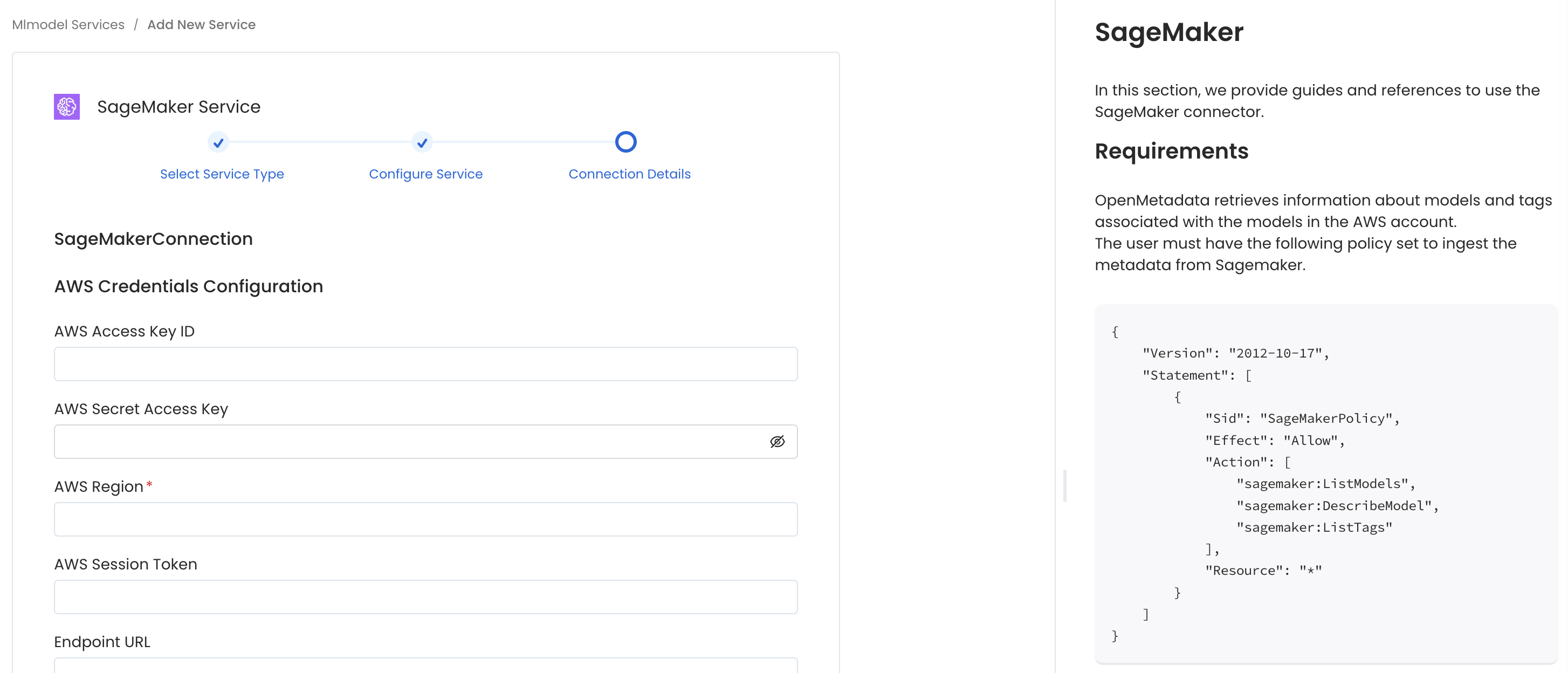
Configure the Service connection by filling the form
Connection Details
- AWS Access Key ID & AWS Secret Access Key: When you interact with AWS, you specify your AWS security credentials to verify who you are and whether you have permission to access the resources that you are requesting. AWS uses the security credentials to authenticate and authorize your requests (docs).
Access keys consist of two parts: An access key ID (for example, AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE), and a secret access key (for example, wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY).
You must use both the access key ID and secret access key together to authenticate your requests.
You can find further information on how to manage your access keys here.
- AWS Region: Each AWS Region is a separate geographic area in which AWS clusters data centers (docs).
As AWS can have instances in multiple regions, we need to know the region the service you want reach belongs to.
Note that the AWS Region is the only required parameter when configuring a connection. When connecting to the services programmatically, there are different ways in which we can extract and use the rest of AWS configurations.
You can find further information about configuring your credentials here.
- AWS Session Token (optional): If you are using temporary credentials to access your services, you will need to inform the AWS Access Key ID and AWS Secrets Access Key. Also, these will include an AWS Session Token.
You can find more information on Using temporary credentials with AWS resources.
- Endpoint URL (optional): To connect programmatically to an AWS service, you use an endpoint. An endpoint is the URL of the entry point for an AWS web service. The AWS SDKs and the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) automatically use the default endpoint for each service in an AWS Region. But you can specify an alternate endpoint for your API requests.
Find more information on AWS service endpoints.
- Profile Name: A named profile is a collection of settings and credentials that you can apply to a AWS CLI command. When you specify a profile to run a command, the settings and credentials are used to run that command. Multiple named profiles can be stored in the config and credentials files.
You can inform this field if you'd like to use a profile other than default.
Find here more information about Named profiles for the AWS CLI.
- Assume Role Arn: Typically, you use
AssumeRolewithin your account or for cross-account access. In this field you'll set theARN(Amazon Resource Name) of the policy of the other account.
A user who wants to access a role in a different account must also have permissions that are delegated from the account administrator. The administrator must attach a policy that allows the user to call AssumeRole for the ARN of the role in the other account.
This is a required field if you'd like to AssumeRole.
Find more information on AssumeRole.
When using Assume Role authentication, ensure you provide the following details:
- AWS Region: Specify the AWS region for your deployment.
- Assume Role ARN: Provide the ARN of the role in your AWS account that OpenMetadata will assume.
- Assume Role Session Name: An identifier for the assumed role session. Use the role session name to uniquely identify a session when the same role is assumed by different principals or for different reasons.
By default, we'll use the name OpenMetadataSession.
Find more information about the Role Session Name.
- Assume Role Source Identity: The source identity specified by the principal that is calling the
AssumeRoleoperation. You can use source identity information in AWS CloudTrail logs to determine who took actions with a role.
Find more information about Source Identity.
6. Test the Connection
Once the credentials have been added, click on Test Connection and Save the changes.
Test the connection and save the Service
7. Configure Metadata Ingestion
In this step we will configure the metadata ingestion pipeline, Please follow the instructions below
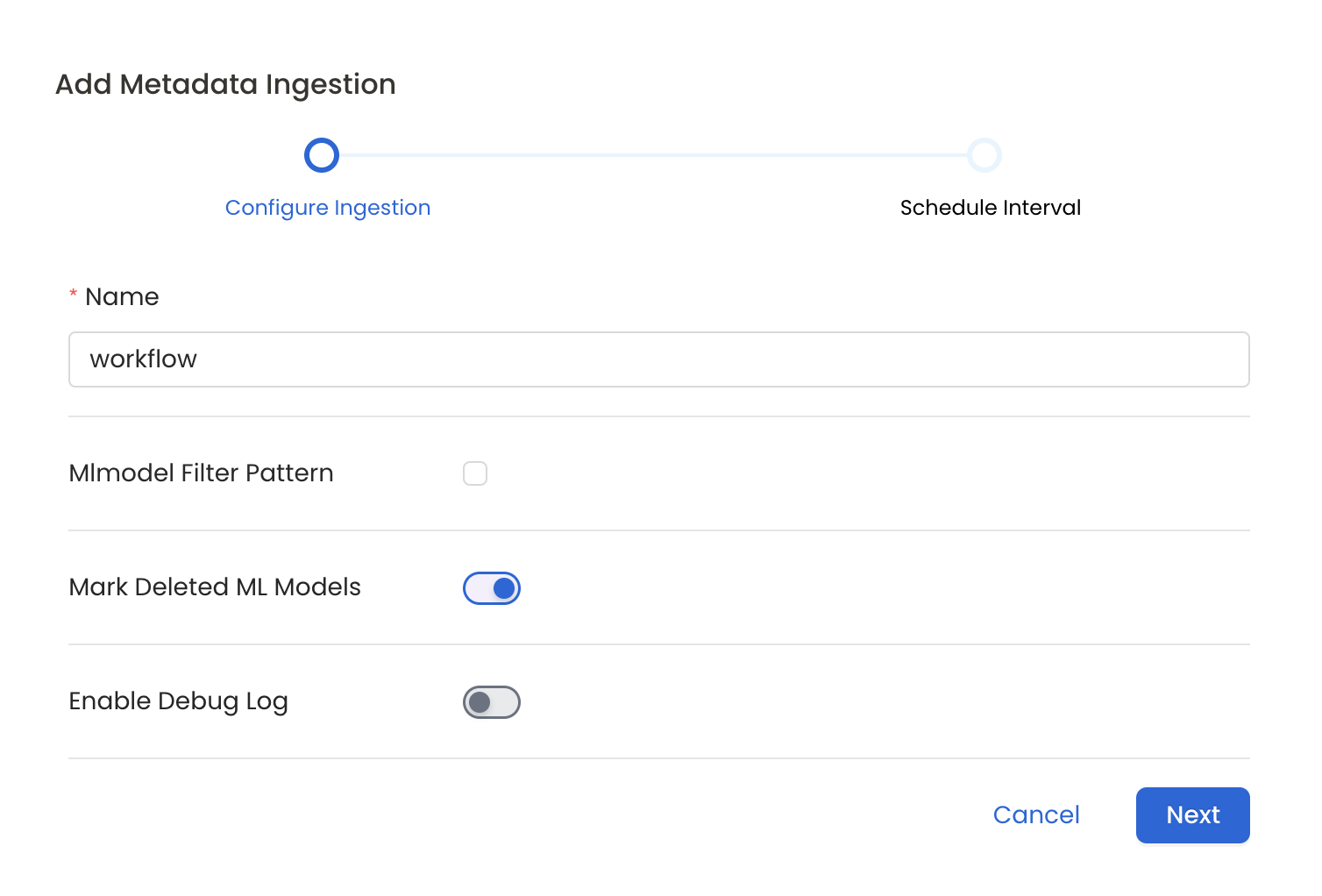
Configure Metadata Ingestion Page
Metadata Ingestion Options
- Name: This field refers to the name of ingestion pipeline, you can customize the name or use the generated name.
- Mark Deleted Ml Models (toggle):: Set the Mark Deleted Ml Models toggle to flag ml models as soft-deleted if they are not present anymore in the source system.
- ML Model Filter Pattern (Optional): To control whether to include an ML Model as part of metadata ingestion.
- Include: Explicitly include ML Models by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Include field. OpenMetadata will include all ML Models with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other ML Models will be excluded.
- Exclude: Explicitly exclude ML Models by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Exclude field. OpenMetadata will exclude all ML Models with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other ML Models will be included.
- Enable Debug Log (toggle): Set the Enable Debug Log toggle to set the default log level to debug.
8. Schedule the Ingestion and Deploy
Scheduling can be set up at an hourly, daily, weekly, or manual cadence. The timezone is in UTC. Select a Start Date to schedule for ingestion. It is optional to add an End Date.
Review your configuration settings. If they match what you intended, click Deploy to create the service and schedule metadata ingestion.
If something doesn't look right, click the Back button to return to the appropriate step and change the settings as needed.
After configuring the workflow, you can click on Deploy to create the pipeline.
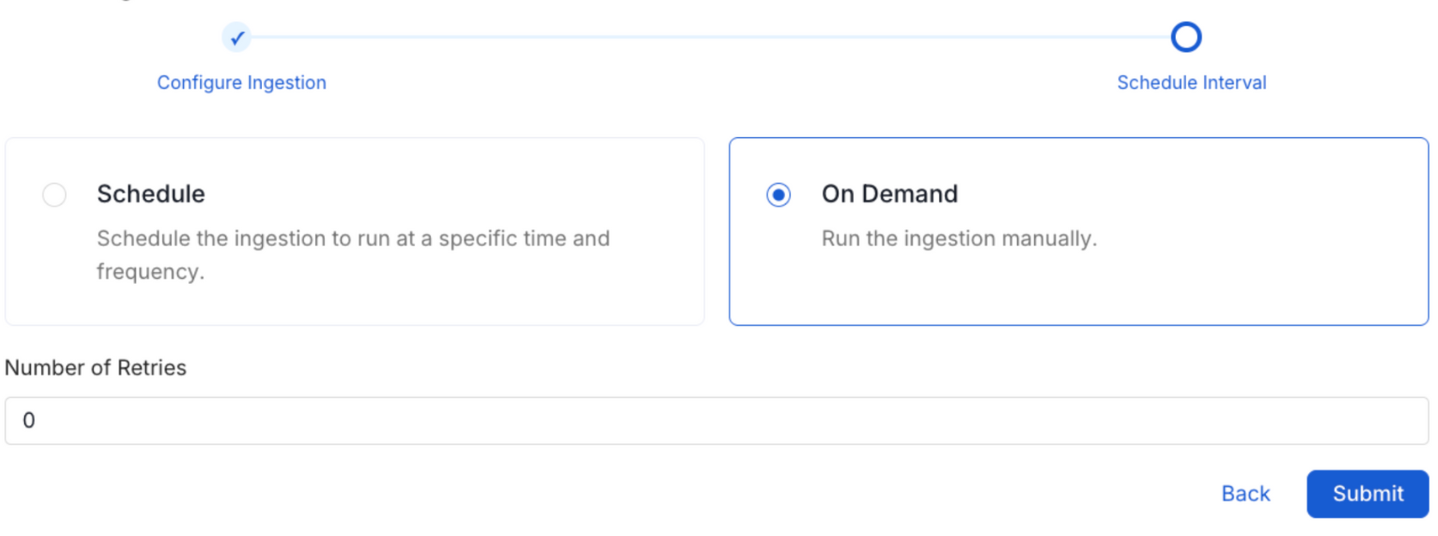
Schedule the Ingestion Pipeline and Deploy
