GKE on Google Cloud Platform Deployment
OpenMetadata supports the Installation and Running of Application on Google Kubernetes Engine through Helm Charts. However, there are some additional configurations which needs to be done as prerequisites for the same.
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) Auto Pilot Mode is not compatible with one of OpenMetadata Dependencies - ElasticSearch. The reason being that ElasticSearch Pods require Elevated permissions to run initContainers for changing configurations which is not allowed by GKE AutoPilot PodSecurityPolicy.
All the code snippets in this section assume the default namespace for kubernetes.
Prerequisites
Cloud Database with CloudSQL and ElasticCloud for GCP as Search Engine
It is recommended to use GCP Cloud SQL services for Database and Elastic Cloud GCP for Search Engine for Production.
We support -
- Cloud SQL (MySQL) engine version 8 or higher
- Cloud SQL (postgreSQL) engine version 12 or higher
- ElasticSearch Engine version 8.X (upto 8.10.X)
We recommend -
- CloudSQL to be Multi Zone Available
- Elastic Cloud Environment with multiple zones and minimum 2 nodes
Once you have the Database and Search Engine configured and available, update the helm values below for OpenMetadata kubernetes deployments to connect with Database and ElasticSearch.
For Database as PostgreSQL, the use the below config for database values -
Persistent Volumes with ReadWriteMany Access Modes
OpenMetadata helm chart depends on Airflow and Airflow expects a persistent disk that support ReadWriteMany (the volume can be mounted as read-write by many nodes).
The workaround is to create nfs-server disk on Google Kubernetes Engine and use that as the persistent claim and deploy OpenMetadata by implementing the following steps in order.
Create NFS Share
Provision GCP Persistent Disk for Google Kubernetes Engine
Run the below command to create a gcloud compute zonal disk. For more information on Google Cloud Disk Options, please visit here.
Deploy NFS Server in GKE
Code Samples
Run the commands below and ensure the pods are running.
We create a ClusterIP Service for pods to access NFS within the cluster at a fixed IP/DNS.
Provision NFS backed PV and PVC for Airflow DAGs and Airflow Logs
Update <NFS_SERVER_CLUSTER_IP> with the NFS Service Cluster IP Address for below code snippets. You can get the clusterIP using the following command
Code Samples for PV and PVC for Airflow DAGs
Create Persistent Volumes and Persistent Volume claims with the below command.
Code Samples for PV and PVC for Airflow Logs
Create Persistent Volumes and Persistent Volume claims with the below command.
Change owner and permission manually on disks
Since airflow pods run as non root users, they would not have write access on the nfs server volumes. In order to fix the permission here, spin up a pod with persistent volumes attached and run it once.
Airflow runs the pods with linux user name as airflow and linux user id as 50000.
Run the below command to create the pod and fix the permissions
Once the permissions pod is up and running, execute the below commands within the container.
Create OpenMetadata dependencies Values
Override openmetadata dependencies airflow helm values to bind the nfs persistent volumes for DAGs and logs.
For more information on airflow helm chart values, please refer to airflow-helm.
When deploying openmeteadata dependencies helm chart, use the below command -
The above command uses configurations defined here. You can modify any configuration and deploy by passing your own values.yaml
Once the openmetadata dependencies helm chart deployed, you can then run the below command to install the openmetadata helm chart -
Troubleshooting
Pods are stuck in Pending State due to Persistent Volume Creation Failure
If you came across invalid access type while creating the pvc, and the permission pod is stuck in "pending" state.
The above error might have occurred due to the pvc volumes not setup or pvc volumes are not mounted properly.
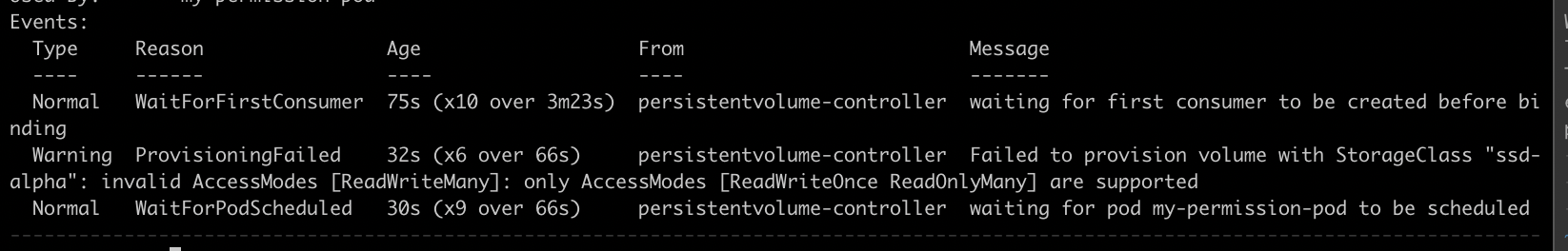
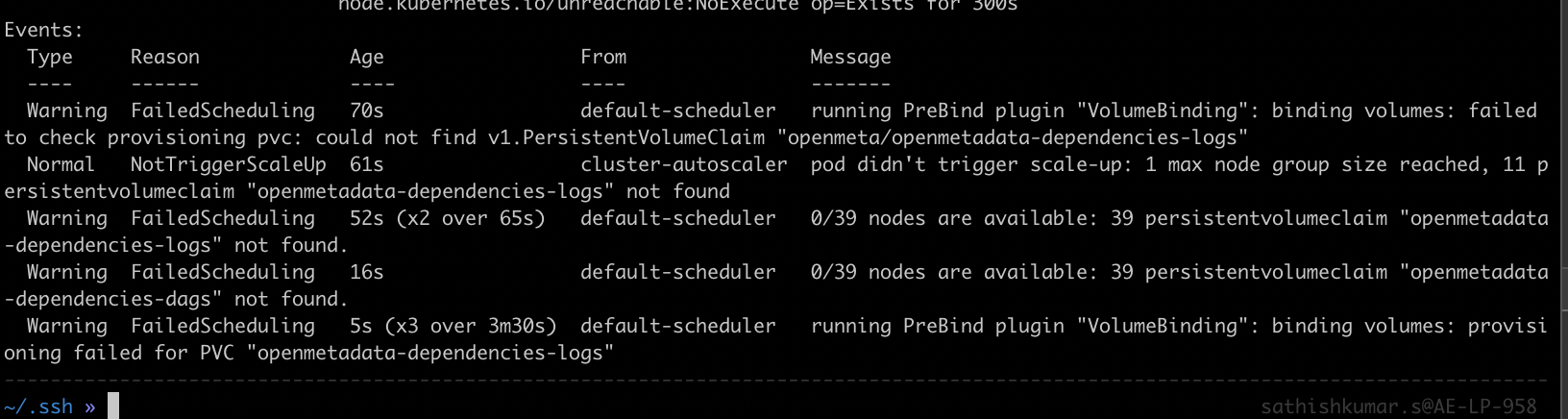
Permission pod events
Please validate:
- all the prerequisites mentioned in this section
- the configuration of
dags_pv_pvc.ymlfile storageClassNamefield in YAML file
FAQs
Java Memory Heap Issue
If your openmetadata pods are not in ready state at any point in time and the openmetadata pod logs speaks about the below issue -
This is due to the default JVM Heap Space configuration (1 GiB) being not enough for your workloads. In order to resolve this issue, head over to your custom openmetadata helm values and append the below environment variable
The flag Xmx specifies the maximum memory allocation pool for a Java virtual machine (JVM), while Xms specifies the initial memory allocation pool.
Upgrade the helm charts with the above changes using the following command helm upgrade --install openmetadata open-metadata/openmetadata --values <values.yml> --namespace <namespaceName>. Update this command your values.yml filename and namespaceName where you have deployed OpenMetadata in Kubernetes.
PostgreSQL Issue permission denied to create extension "pgcrypto"
If you are facing the below issue with PostgreSQL as Database Backend for OpenMetadata Application,
It seems the Database User does not have sufficient privileges. In order to resolve the above issue, grant usage permissions to the PSQL User.
In the above command, replace <openmetadata_psql_user> with the sql user used by OpenMetadata Application to connect to PostgreSQL Database.
How to extend and use custom docker images with OpenMetadata Helm Charts ?
Extending OpenMetadata Server Docker Image
1. Create a Dockerfile based on docker.getcollate.io/openmetadata/server
OpenMetadata helm charts uses official published docker images from DockerHub. A typical scenario will be to install organization certificates for connecting with inhouse systems.
For Example -
where docker.getcollate.io/openmetadata/server:x.y.z needs to point to the same version of the OpenMetadata server, for example docker.getcollate.io/openmetadata/server:1.3.1. This image needs to be built and published to the container registry of your choice.
2. Update your openmetadata helm values yaml
The OpenMetadata Application gets installed as part of openmetadata helm chart. In this step, update the custom helm values using YAML file to point the image created in the previous step. For example, create a helm values file named values.yaml with the following contents -
3. Install / Upgrade your helm release
Upgrade/Install your openmetadata helm charts with the below single command:
Extending OpenMetadata Ingestion Docker Image
One possible use case where you would need to use a custom image for the ingestion is because you have developed your own custom connectors. You can find a complete working example of this here. After you have your code ready, the steps would be the following:
1. Create a Dockerfile based on docker.getcollate.io/openmetadata/ingestion:
For example -
where docker.getcollate.io/openmetadata/ingestion:x.y.z needs to point to the same version of the OpenMetadata server, for example docker.getcollate.io/openmetadata/ingestion:1.3.1. This image needs to be built and published to the container registry of your choice.
2. Update the airflow in openmetadata dependencies values YAML
The ingestion containers (which is the one shipping Airflow) gets installed in the openmetadata-dependencies helm chart. In this step, we use our own custom values YAML file to point to the image we just created on the previous step. You can create a file named values.deps.yaml with the following contents:
3. Install / Upgrade helm release
Upgrade/Install your openmetadata-dependencies helm charts with the below single command:
How to disable MySQL and ElasticSearch from OpenMetadata Dependencies Helm Charts ?
If you are using MySQL and ElasticSearch externally, you would want to disable the local installation of mysql and elasticsearch while installing OpenMetadata Dependencies Helm Chart. You can disable the MySQL and ElasticSearch Helm Dependencies by setting enabled: false value for each dependency. Below is the command to set helm values from Helm CLI -
Alternatively, you can create a custom YAML file named values.deps.yaml to disable installation of MySQL and Elasticsearch .
How to configure external database like PostgreSQL with OpenMetadata Helm Charts ?
OpenMetadata Supports PostgreSQL as one of the Database Dependencies. OpenMetadata Helm Charts by default does not include PostgreSQL as Database Dependencies. In order to configure Helm Charts with External Database like PostgreSQL, follow the below guide to make the helm values change and upgrade / install OpenMetadata helm charts with the same.
Upgrade Airflow Helm Dependencies Helm Charts to connect to External Database like PostgreSQL
We ship airflow-helm as one of OpenMetadata Dependencies with default values to connect to MySQL Database as part of externalDatabase configurations.
You can find more information on setting the externalDatabase as part of helm values here.
With OpenMetadata Dependencies Helm Charts, your helm values would look something like below -
For the above code, it is assumed you are creating a kubernetes secret for storing Airflow Database login Credentials. A sample command to create the secret will be kubectl create secret generic airflow-postgresql-secrets --from-literal=airflow-postgresql-password=<password>.
Upgrade OpenMetadata Helm Charts to connect to External Database like PostgreSQL
Update the openmetadata.config.database.* helm values for OpenMetadata Application to connect to External Database like PostgreSQL.
With OpenMetadata Helm Charts, your helm values would look something like below -
For the above code, it is assumed you are creating a kubernetes secret for storing OpenMetadata Database login Credentials. A sample command to create the secret will be kubectl create secret generic openmetadata-postgresql-secrets --from-literal=openmetadata-postgresql-password=<password>.
Once you make the above changes to your helm values, run the below command to install/upgrade helm charts -
How to customize OpenMetadata Dependencies Helm Chart with custom helm values
Our OpenMetadata Dependencies Helm Charts are internally depends on three sub-charts -
- Bitnami MySQL (helm chart version 9.7.2)
- OpenSearch (helm chart version 2.12.2)
- Airflow (helm chart version 8.8.0)
If you are looking to customize the deployments of any of the above dependencies, please refer to the above links for customizations of helm values for further references.
By default, OpenMetadata Dependencies helm chart provides initial generic customization of these helm values in order to get you started quickly. You can refer to the openmetadata-dependencies helm charts default values here.