Overview of the Incident Manager
Using Incident Manager, managing data quality issues becomes streamlined and efficient. By centralizing the resolution process, assigning tasks, and logging root causes, your team can quickly address and resolve failures. The historical record of past incidents serves as a comprehensive guide, aiding your team in troubleshooting and resolving issues more effectively. All the necessary context is readily available, making it easier to maintain high data quality standards.
Opening and Triaging Incidents
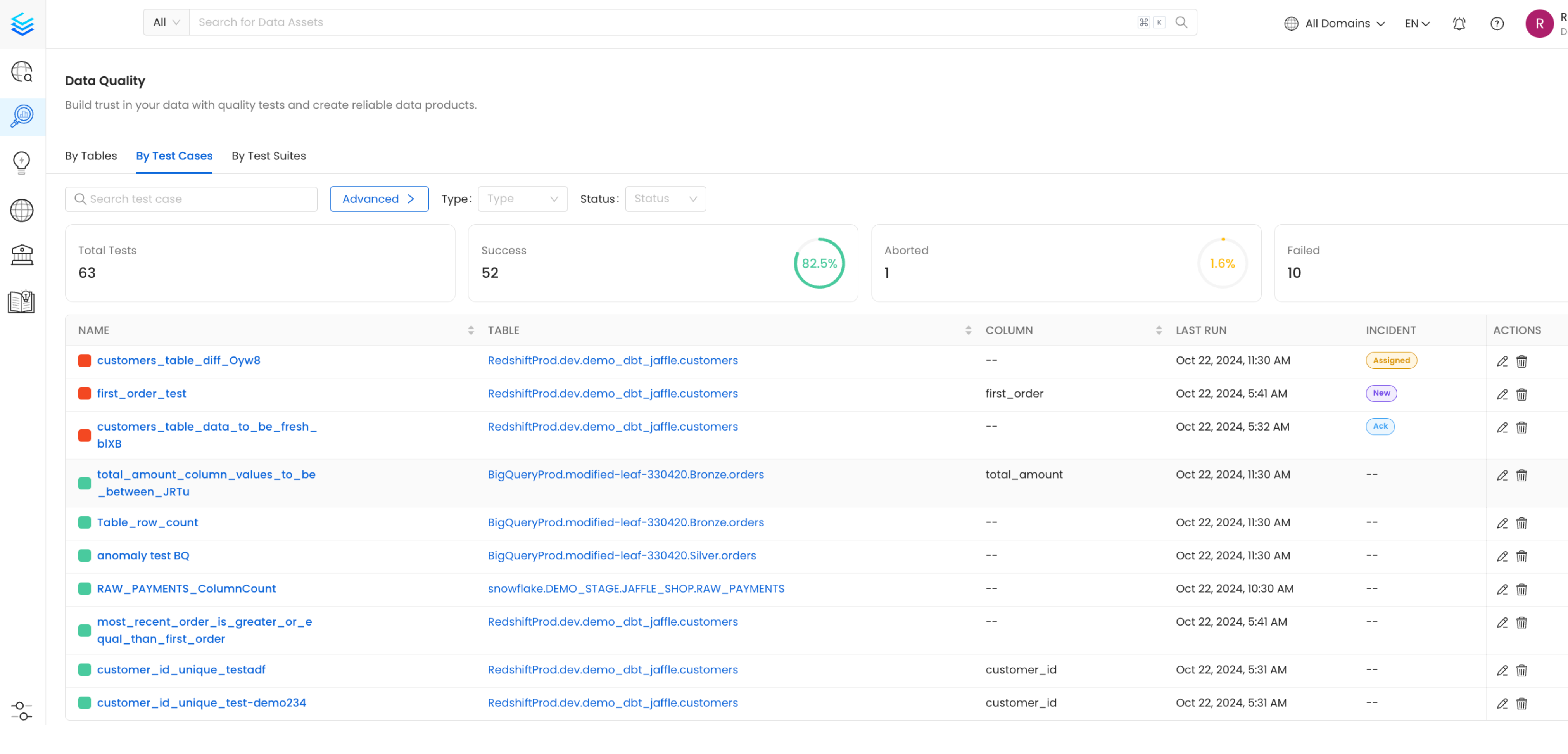
In v1.1.0, we introduced the ability for user to manage and triage incidents linked to failures. When a test case fails, it will automatically open a new incident and mark it as new. If enough information is available, OpenMetadata will automatically assign a severity to the incident; note that you can override this severity. It indicates that a new failure has happened.
Test suite results table
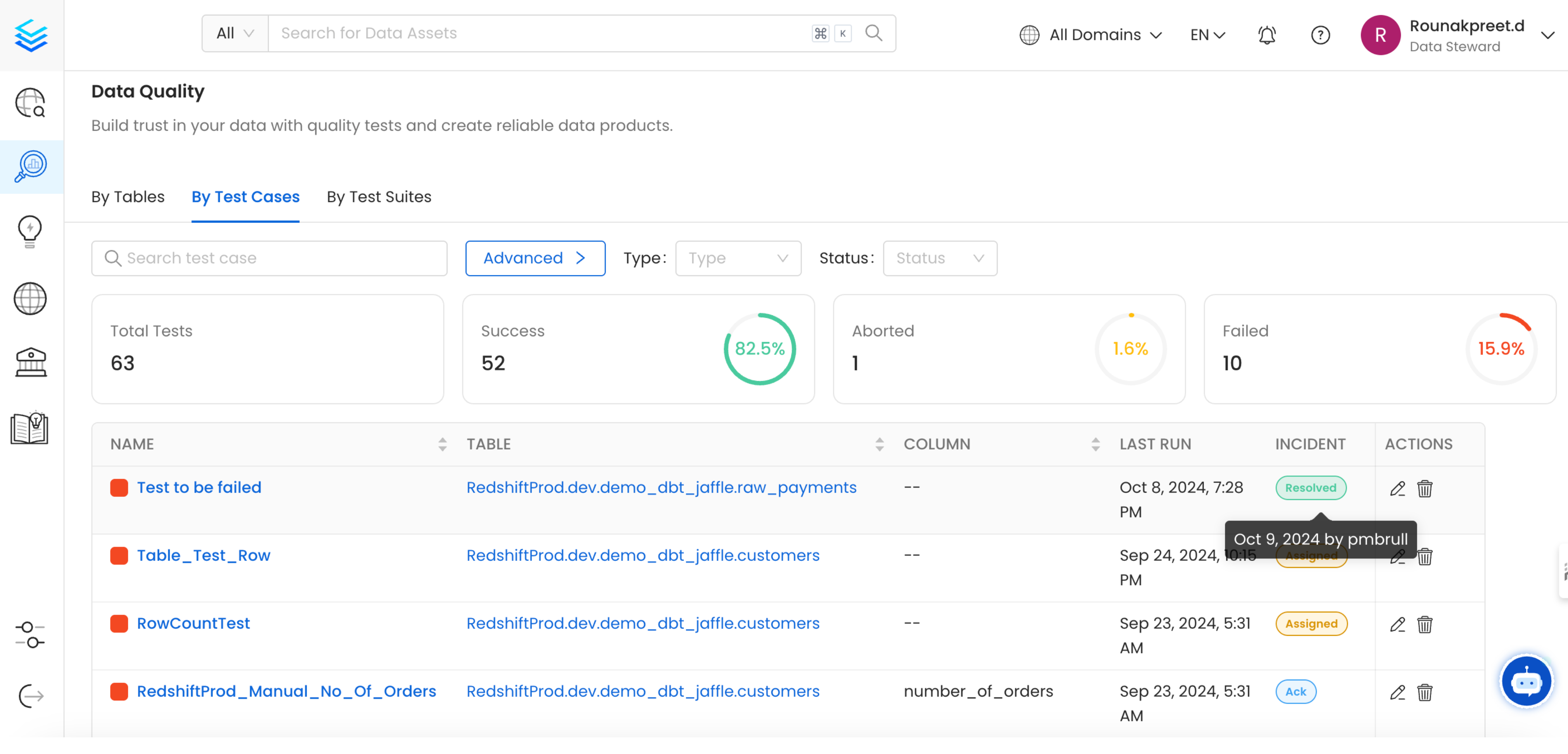
The Incident Manager serves as a centralized hub to handle the resolution flow of failed Data Quality Tests. Once an incident has been open you will be able to triage and manage it. You can perform different actions at this stage:
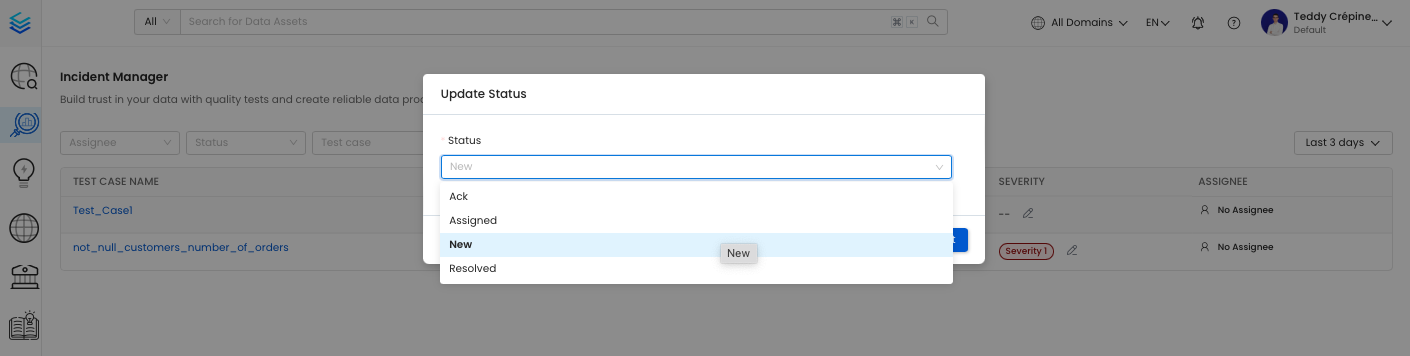
- Acknowledge the Issue: Recognize and confirm that there is a problem that needs attention. By marking with
ackyou can inform users that people are aware of the ongoing incident. - Assign Responsibility: Designate a specific person or team to address the errors. By marking with
assignyou can open a task for the assignee. - Log the Root Cause: Document the underlying cause of the failure for future reference and analysis.
Test suite results table
Test suite results table
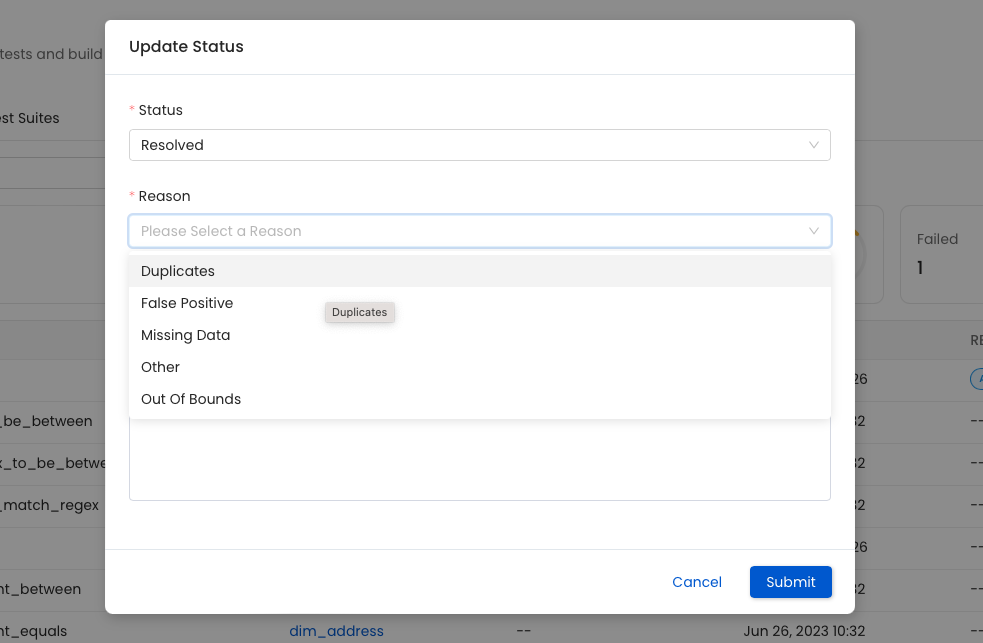
You can mark the incident as resolved. The user will be required to specify the reason and add a comment. This provides context regarding the incident and helps users further understand what might have gone wrong
Test suite results table
Test suite results table
Using the Test Resolution Flow
The Test Resolution flow is a critical feature of the Incident Manager. Here’s how it works:
- Failure Notification: When a Data Quality Test fails, the system generates a notification.
- Acknowledge the Failure: The designated user acknowledges the issue within the Incident Manager.
- Assignment: The issue is then assigned to a knowledgeable user or team responsible for resolving it.
- Status Updates: The assigned user can update the status of the issue, keeping the organization informed about progress and any developments.
- Sharing Updates: All impacted users receive updates, ensuring everyone stays informed about the resolution process.
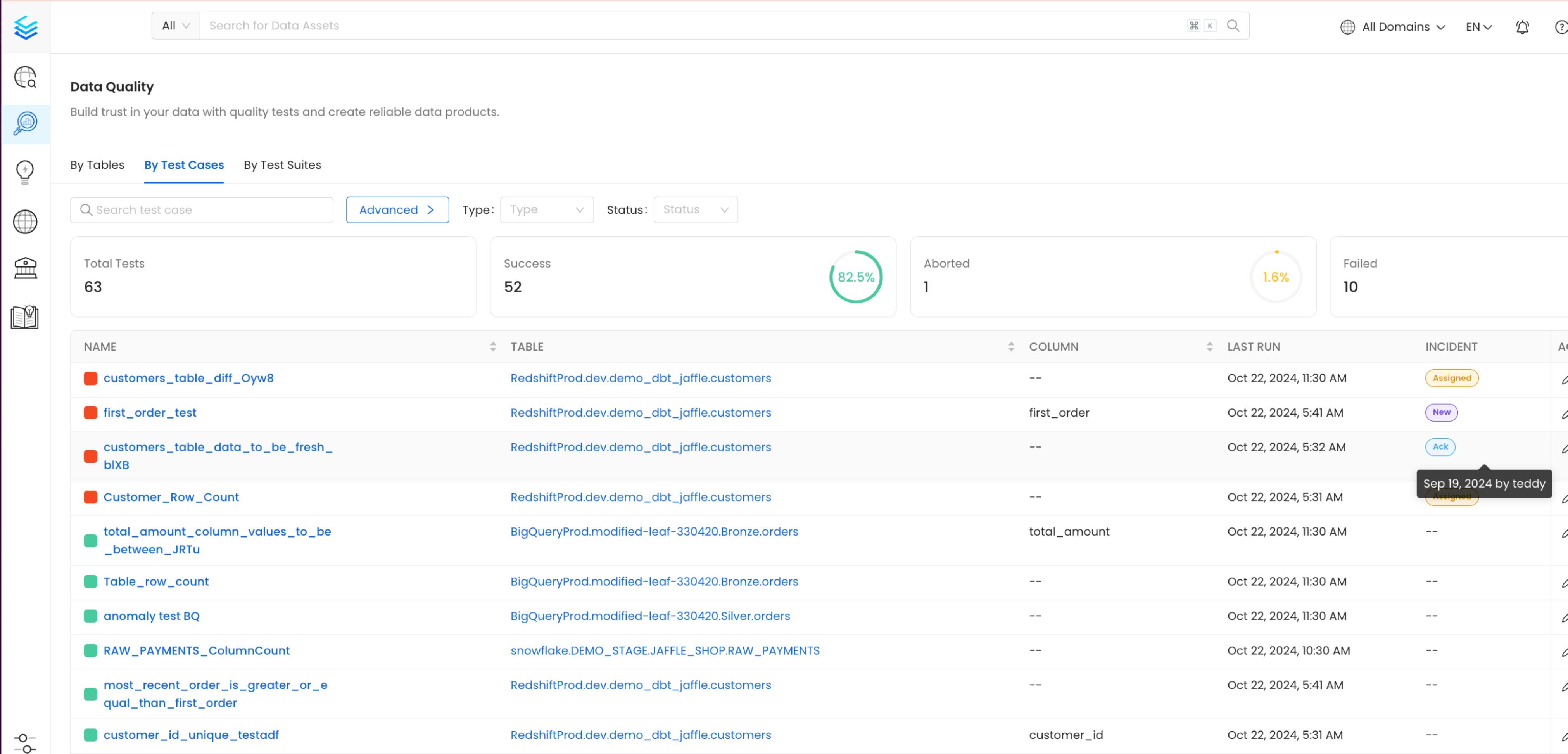
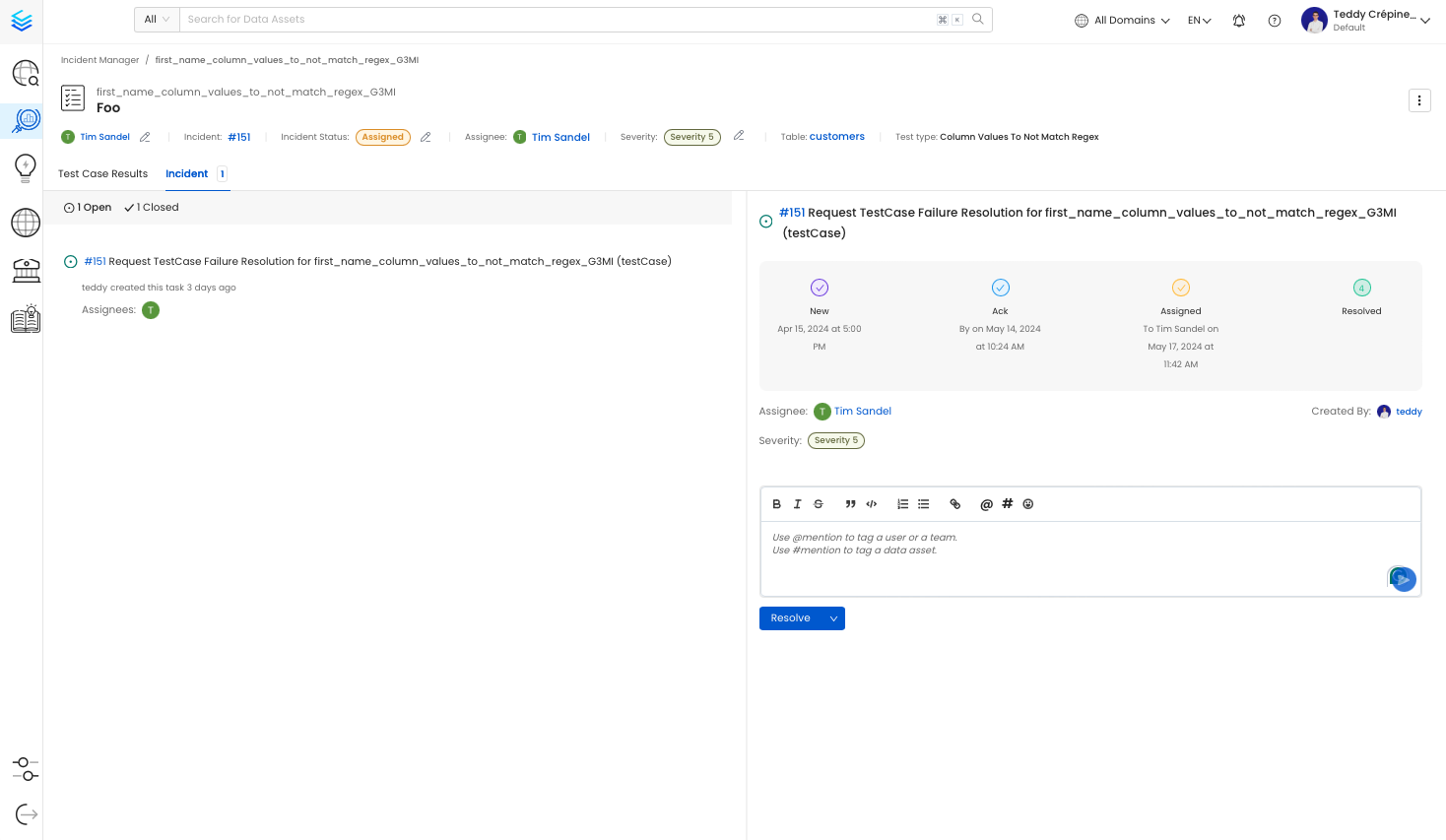
Incidents Context & History
When clicking on an open incident you will different information: Open Incident: this section will show you open incidents with the timeline and any comments/collaboration that might have been happening. Closed Incidents: this section will show you incidents that have been resolved in the past with the timeline and any comments/collaboration that might have been happening and the resolution reason.
Test suite results table
Building a Troubleshooting Handbook
One of the powerful features of the Incident Manager is its ability to store all past failures. This historical data becomes a valuable troubleshooting handbook for your team. Here's how you can leverage it:
- Explore Similar Scenarios: Review previous incidents to understand how similar issues were resolved.
- Contextual Information: Access all necessary context directly within OpenMetadata, including previous resolutions, root causes, and responsible teams.
- Continuous Improvement: Use historical data to improve data quality tests and prevent future failures.
Steps to Get Started
- Access the Incident Manager: Navigate to the Incident Manager within the OpenMetadata platform.
- Monitor Data Quality Tests: Keep an eye on your data quality tests to quickly identify any failures.
- Acknowledge and Assign: Acknowledge any issues promptly and assign them to the appropriate team members.
- Log and Learn: Document the root cause of each failure and use the stored information to learn and improve.
By following these steps, you'll ensure that your organization effectively manages data quality issues, maintains high standards, and continuously improves its data quality processes.