Local Docker Deployment
This installation doc will help you start a OpenMetadata standalone instance on your local machine.
If you'd rather see the steps in a guided tutorial, we've got you covered! Otherwise, feel free to read the content below 👇
Requirements (OSX, Linux and Windows)
Please ensure your host system meets the requirements listed below. Then continue to the Procedure for installing OpenMetadata.
OSX and Linux
Docker (version 20.10.0 or greater)
Docker is an open-source platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. It enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure, so you can deliver software quickly using OS-level virtualization. It helps deliver software in packages called Containers.
To check the version of Docker you have, use the following command.
If you need to install Docker, please visit Get Docker.
You must allocate at least 6 GiB of memory and 4 vCPUs to Docker in order to run OpenMetadata. To change the memory allocation for Docker, please visit Preferences -> Resources -> Advanced in your Docker Desktop.
Docker Compose (version v2.1.1 or greater)
The Docker compose package enables you to define and run multi-container Docker applications. The compose command integrates compose functions into the Docker platform, making them available from the Docker command-line interface ( CLI). The Python packages you will install in the procedure below use compose to deploy OpenMetadata.
- MacOS X: Docker on MacOS X ships with compose already available in the Docker CLI.
- Linux: To install compose on Linux systems, please visit the Docker CLI command documentation and follow the instructions.
To verify that the docker compose command is installed and accessible on your system, run the following command.
Upon running this command you should see output similar to the following.
Install Docker Compose Version 2.0.0 on Linux
Follow the instructions here to install docker compose version 2.0.0
Run the following command to download the current stable release of Docker Compose
This command installs Compose V2 for the active user under $HOME directory. To install Docker Compose for all users on your system, replace
~/.docker/cli-pluginswith/usr/local/lib/docker/cli-plugins.Apply executable permissions to the binary
Test your installation
Windows
WSL2, Ubuntu 20.04, and Docker for Windows
- Install WSL2
- Install Ubuntu 20.04
- Install Docker for Windows
- Once installed, please follow the steps here and complete all the pre-requisites for a seamless installation and deployment.
- After completion of the pre-requisites, please install
python3-pipandpython3-venvon your Ubuntu system.- Command:
apt install python3-pip python3-venv(Ensure that you have the privilege to install packages, if not, please use Super User.)
- Command:
Procedure
1. Create a directory for OpenMetadata
Create a new directory for OpenMetadata and navigate into that directory.
2. Download Docker Compose File from GitHub Releases
Download the docker-compose.yml file from the release page here.
The latest version is at the top of the page
- Deploying with MySQL: Download
docker-compose.ymlfile from the above link. - Deploying with PostgreSQL: Download
docker-compose-postgres.ymlfile from the above link.
You can use the curl or wget command as well to fetch the docker compose files from your terminal -
3. Start the Docker Compose Services
Run the below command to deploy the OpenMetadata
For OpenMetadata with MySQL Database -
For OpenMetadata with PostgreSQL Database -
These commands will pull the docker images of Openmetadata for MySQL / PostgreSQL, OpenMetadata-Server, OpenMetadata-Ingestion and Elasticsearch.
Upon running this command you should see output similar to the following.
You can validate that all containers are up by running with command docker ps.
In a few seconds, you should be able to access the OpenMetadata UI at http://localhost:8585
By default, we ship Docker Compose with host and docker named volume mapping for MySQL, PostgreSQL, ElasticSearch and Ingestion Services with quickstart docker compose services. This will be available under docker-volume directory on host machine in the same path as docker compose files.
Log in to OpenMetadata
OpenMetadata provides a default admin account to login.
You can access OpenMetadata at http://localhost:8585. Use the following credentials to log in to OpenMetadata.
- Username:
admin@open-metadata.org - Password:
admin
Once you log in, you can goto Settings -> Users to add another user and make them admin as well.
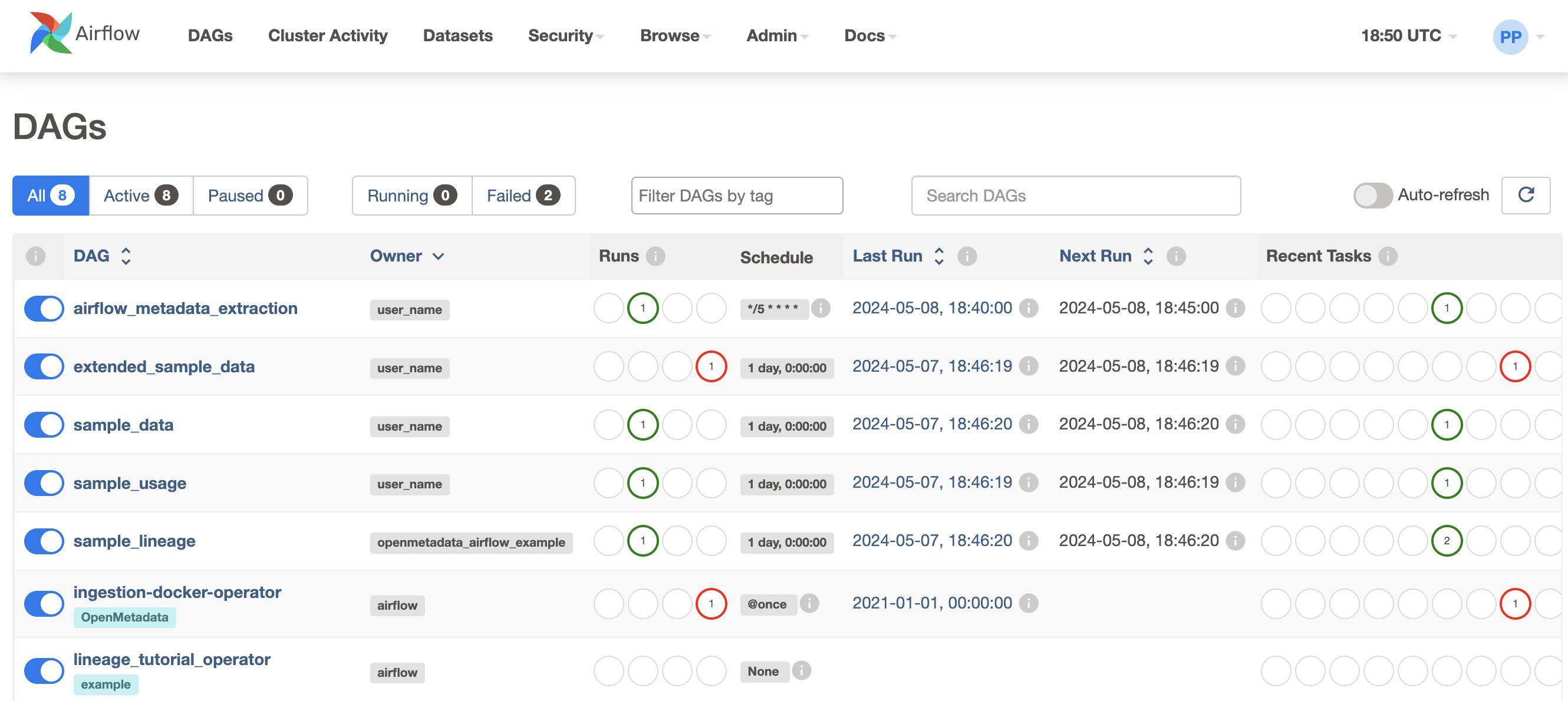
Log in to Airflow
OpenMetadata ships with an Airflow container to run the ingestion workflows that have been deployed via the UI.
In the Airflow, you will also see some sample DAGs that will ingest sample data and serve as an example.
You can access Airflow at http://localhost:8080. Use the following credentials to log in to Airflow.
- Username:
admin - Password:
admin
Customizing Airflow Admin Credentials:
When using Docker Compose, you can change the default Airflow admin credentials by setting the following environment variables:
- Username:
AIRFLOW_ADMIN_USER - Password:
AIRFLOW_ADMIN_PASSWORD
Airflow DAGs Showcased in Deployment
You can explore the examples of Airflow DAGs used with OpenMetadata. Refer here for more information.
Go on a tour and start discovering the power of metadata & collaboration
Start and Stop
From the same directory mentioned in step 1, use the following commands to start and stop the Docker Compose services.
To stop the services
To start the services
Start and stop are used to completely halt or restart the running services. When services are stopped, their containers are shut down but remain available for restarting without rebuilding. Importantly, any data stored in Docker volumes remains unaffected during this process. The volumes stay intact and accessible, preserving your application’s state and making it easy to restart the services without losing data. This makes it a reliable option for temporary shutdowns while maintaining continuity.
Cleanup
To stop the Docker Compose services, run the following command from the same directory mentioned in step 1.
Stop the services
If you want to clean up the associated named volumes as well, use the following command
Named volumes are used to persist data created by containers, ensuring that the data remains even after the containers are stopped or removed. These volumes are managed by Docker and stored independently from the containers.
Using the --volumes flag with the docker compose down command will delete these volumes, permanently removing all stored data.
Troubleshooting
Compose is not a docker command
If you are getting an error such as "compose" is not a docker command, you might need to revisit the installation steps above to make sure that Docker Compose is properly added to your system.
Network openmetadata_app_net Error
You might see something like:
A common solution is to run docker network prune:
So be careful if you want to keep up some (unused) networks from your laptop.
Connect Host Services from Docker Container
You can connect Docker containers to communicate with Host Operating System Services. Navigate to the official docker documentation which will help achieve the same.
Security
Please follow our Enable Security Guide to configure security for your OpenMetadata installation.
Next Steps
- Refer the How-to Guides for an overview of all the features in OpenMetadata.
- Visit the Connectors documentation to see what services you can integrate with OpenMetadata.
- Visit the API documentation and explore the rich set of OpenMetadata APIs.
Volume Permissions: Operation not permitted
If you are running on Windows (WSL2) and see permissions errors when starting the databases (either MySQL or Postgres), e.g.,
You can try to update the /etc/wsl.conf file from the WSL2 machine to add: