Elasticsearch
PRODFeature List
✓ Search Indexes
✓ Sample Data
Requirements
We support Elasticsearch 7.0 and above. We extract Elasticsearch’s metadata by using its API. To run this ingestion, you just need a user with permissions to the ElasticSearch instance.Metadata Ingestion
Visit the Services Page
Click `Settings` in the side navigation bar and then `Services`. The first step is to ingest the metadata from your sources. To do that, you first need to create a Service connection first. This Service will be the bridge between OpenMetadata and your source system. Once a Service is created, it can be used to configure your ingestion workflows.

Name and Describe your Service
Provide a name and description for your Service.
Service Name
OpenMetadata uniquely identifies Services by their **Service Name**. Provide a name that distinguishes your deployment from other Services, including the other ElasticSearch Services that you might be ingesting metadata from. Note that when the name is set, it cannot be changed.
Connection Details
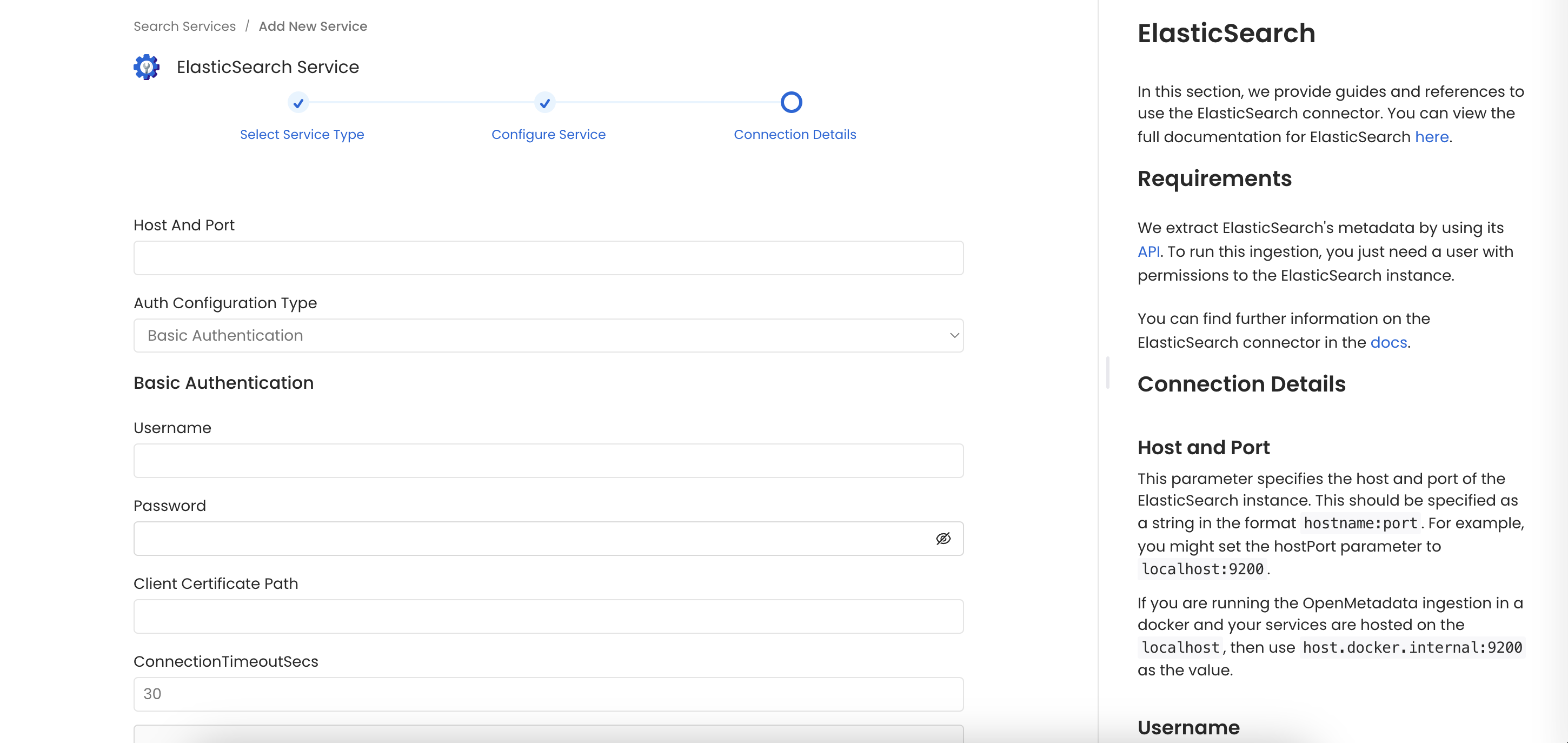
Connection Details
- Host and Port: This parameter specifies the host and port of the Elasticsearch instance. This should be specified as a URI string in the format
http://hostname:portorhttps://hostname:port. For example, you might set it tohttps://localhost:9200. - Authentication Types:
- Basic Authentication
- Username: Username to connect to Elasticsearch required when Basic Authentication is enabled on Elasticsearch.
- Password: Password of the user account to connect with Elasticsearch.
- API Key Authentication
- API Key: API Key to connect to Elasticsearch required when API Key Authentication is enabled on Elasticsearch.
- API Key Id: Enter API Key ID In case of API Key Authentication if there is any API Key ID associated with the API Key, otherwise this field can be left blank.
- SSL Certificates:
- SSL Certificates By Path
- CA Certificate Path: This field specifies the path of CA certificate required for authentication.
- Client Certificate Path: This field specifies the path of Clint certificate required for authentication.
- Private Key Path: This field specifies the path of Clint Key/Private Key required for authentication.
- SSL Certificates By Value
- CA Certificate Value: This field specifies the value of CA certificate required for authentication.
- Client Certificate Value: This field specifies the value of Clint certificate required for authentication.
- Private Key Value: This field specifies the value of Clint Key/Private Key required for authentication.
- Staging Directory Path: This field specifies the path to temporary staging directory, where the certificates will be stored temporarily during the ingestion process, which will de deleted once the ingestion job is over.
- when you are using this approach make sure you are passing the key in a correct format. If your certificate looks like this:
You will have to replace new lines with\nand the final value that you need to pass should look like this: - Connection Timeout in Seconds: Connection timeout configuration for communicating with Elasticsearch APIs.
Test the Connection
Once the credentials have been added, click on Test Connection and Save the changes.

Configure Metadata Ingestion
In this step we will configure the metadata ingestion pipeline,
Please follow the instructions below

Metadata Ingestion Options
- Name: This field refers to the name of ingestion pipeline, you can customize the name or use the generated name.
- Search Index Filter Pattern (Optional): Use to search index filter patterns to control whether or not to include search index as part of metadata ingestion.
- Include: Explicitly include search index by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Include field. OpenMetadata will include all search indexes with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other schemas will be excluded.
- Exclude: Explicitly exclude search index by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Exclude field. OpenMetadata will exclude all search indexes with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other schemas will be included.
- Include Sample Data (toggle): Set the Ingest Sample Data toggle to control whether to ingest sample data as part of metadata ingestion.
- Sample Size: If include sample data is enabled, 10 records will be ingested by default. Using this field you can customize the size of sample data.
- Include Index Templates (toggle): Set the Include Index Templates toggle to control whether to include index templates as part of metadata ingestion.
- Override Metadata: Set the Override Metadata toggle to control whether to override the metadata if it already exists.
- Enable Debug Log (toggle): Set the Enable Debug Log toggle to set the default log level to debug.
Schedule the Ingestion and Deploy
Scheduling can be set up at an hourly, daily, weekly, or manual cadence. The
timezone is in UTC. Select a Start Date to schedule for ingestion. It is
optional to add an End Date.Review your configuration settings. If they match what you intended,
click Deploy to create the service and schedule metadata ingestion.If something doesn’t look right, click the Back button to return to the
appropriate step and change the settings as needed.After configuring the workflow, you can click on Deploy to create the
pipeline.